
Disconnect switches, also known as isolator switches, serve as crucial devices that de-energize electrical circuits, enabling safe maintenance and operation of equipment. They provide a visible means of disconnect and act as the first line of defense in electrical safety protocols. These switches are commonly positioned upstream of power distribution systems and function as control points during electrical faults or shutdowns.
For more info please visit: https://market.us/report/disconnect-switches-market/
In industrial settings, disconnect switches are indispensable. From safeguarding factory automation systems to isolating high-voltage panels in data centers, these switches are pivotal for compliance, uptime, and worker safety. In commercial buildings, they serve HVAC units, elevators, and emergency lighting systems, ensuring isolation and controlled serviceability without disrupting entire grids.
The ongoing wave of industrial digitization has supercharged the demand for robust electrical infrastructure. Disconnect switches, being central to circuit protection, have witnessed surging adoption. From smart factories in Germany to automotive plants in Japan, automation relies on modular, easily maintainable switchgear that supports seamless load disconnection.
Stringent occupational safety laws like OSHA in the U.S. and the European Machinery Directive necessitate the use of disconnect switches in numerous applications. Regulatory enforcement compels manufacturers and facility managers to install certified isolation solutions, driving consistent demand across geographies and sectors.
Solar and wind energy farms often operate in remote, high-voltage environments. Disconnect switches ensure that maintenance teams can work safely without exposure to live systems. The global renewable energy transition is catalyzing demand for high-voltage DC and AC disconnects across utility-scale projects.
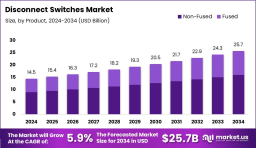
Fused disconnects integrate overcurrent protection within the device, ideal for systems requiring integrated fault interruption. Non-fused variants, on the other hand, are simpler and cost-effective, mainly used where protection is handled elsewhere in the circuit. Market preference often hinges on application specificity and budget constraints.
Panel-mounted disconnects dominate industrial control cabinets, while DIN rail variants suit modular switchboards and compact enclosures. Wall-mounted units are prevalent in outdoor or rooftop installations. The proliferation of custom electrical enclosures has spurred a rise in form-factor innovations across all styles.
Utilities deploy disconnects at substations and feeder networks to manage grid loads and ensure fault isolation. In manufacturing, they support conveyor systems, robotics, and machining operations. Data centers employ them to control mission-critical power distribution units (PDUs), enabling isolated shutdowns during servicing.
Aging infrastructure in the United States and Canada fuels replacement demand. Many commercial and industrial facilities are retrofitting legacy electrical systems with advanced disconnects to meet modern safety codes and improve operational resilience, creating a robust aftermarket.
Countries like India, China, and Vietnam are undergoing aggressive industrialization. Power distribution networks are expanding at a rapid clip, generating substantial demand for disconnect switches. OEMs are establishing local manufacturing to cater to high-volume, cost-sensitive projects.
Europe’s ambitious clean energy targets have made it a hotbed for smart grid development. Disconnect switches here are evolving into intelligent components capable of remote monitoring and integration with digital energy platforms. The EU’s focus on decarbonization is feeding long-term market stability.
For more info please visit: https://market.us/report/disconnect-switches-market/
Schneider Electric, ABB, Eaton, Siemens, and Legrand dominate the landscape, competing through product breadth, regional penetration, and after-sales service. Strategic acquisitions, such as niche isolator manufacturers or local distributors, are accelerating portfolio expansion.
The future lies in intelligent disconnect switches—devices equipped with IoT sensors, diagnostics, and remote operation capabilities. These smart switches enable predictive maintenance and grid transparency, aligning with broader trends in Industry 4.0 and energy digitization.
The disconnect switches market is projected to exhibit steady growth through 2030, underpinned by industrial electrification, grid modernization, and renewable energy proliferation. Emerging markets and hybrid switchgear solutions present fertile grounds for innovation and expansion.
Conclusion
Disconnect switches, though unassuming, are silent sentinels of modern electrical systems. As global infrastructure evolves toward safer, smarter, and more sustainable paradigms, these devices will remain foundational to electrical integrity and resilience across industries.
| No comments yet. Be the first. |