
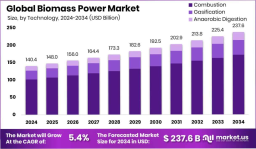
The global biomass power market is on a steady growth path, expected to rise from USD 140.4 billion in 2024 to USD 237.6 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.4%. Biomass power is produced by using natural waste materials such as wood chips, crop leftovers, and even household waste to generate electricity. This is done through methods like burning, gasification, or digestion, which turn organic matter into energy. The market involves everything from collecting raw materials to delivering electricity, and it plays an essential role in both renewable energy expansion and waste reduction worldwide.
The push for clean energy and better waste handling systems is giving biomass power strong momentum. Government incentives, including feed in tariffs and support for low carbon energy, are making it easier to invest in biomass projects. In 2024, combustion technology dominated the market with 72.4% share, and solid biofuels like wood pellets made up 67.3% of the fuel used. Industrial sectors were the biggest users, taking up 54.7% of the market. Europe led the way with USD 64.3 billion in market value, thanks to its strong climate goals and reliable energy infrastructure.
The global biomass power market will grow from USD 140.4 billion (2024) to USD 237.6 billion (2034).
Combustion technology held the largest share in 2024 at 72.4%.
Solid biofuels like wood chips and pellets made up 67.3% of feedstock use.
Industrial applications led the market with a 54.7% share.
Europe topped the regional market, valued at USD 64.3 billion in 2024.

Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/global-biomass-power-market/free-sample/
Governments worldwide are supporting biomass energy with favorable policies, making it easier to invest in these projects.
The growing demand for cleaner, renewable energy is pushing industries to shift away from fossil fuels.
Availability of cheap and abundant organic waste in rural and farming areas ensures a steady fuel supply.
Biomass helps solve two big problems—managing waste and producing clean energy at the same time.
Retrofitting old coal plants to run on biomass can cut emissions and make use of existing infrastructure.
Developing countries in Asia-Pacific and Latin America offer untapped markets with rich biomass resources.
Technological advancements like gasification and digestion are opening up new, more efficient energy pathways.
Collaborating with agriculture and waste industries can improve feedstock availability and reduce costs.
Building biomass power plants requires large upfront investment, which may discourage small players.
Feedstock supply can be inconsistent due to seasonal changes and storage challenges.
Competing renewable options like solar and wind are often cheaper and easier to manage.
Environmental concerns about land use and carbon output from biomass transport may lead to regulation issues.
While combustion is still the most used method, cleaner technologies like gasification are catching up fast.
Solid biofuels remain the most common feedstock due to their reliability and availability.
Industrial sectors continue to be the biggest users of biomass power due to their large energy needs.
Europe maintains its lead in the market thanks to strong green policies and existing infrastructure.
| No comments yet. Be the first. |