
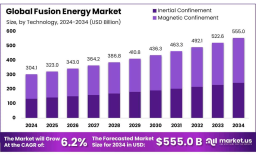
The global fusion energy market is on track to grow from USD 304.1 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 555.0 billion by 2034, advancing at a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% during the forecast period.A key driver of this growth is the widespread adoption of magnetic confinement technology, which accounts for over 56.3% of the market share due to its successful integration into systems like tokamaks and stellarators.
Alongside this, deuterium-tritium (D-T) fuel remains the top choice, making up roughly 63.5% of the market, thanks to its high energy output and familiarity within the scientific community. With consistent public and private investments, fusion energy is moving from theoretical science to practical, large-scale energy solutions. The market is experiencing stable momentum, signaling strong potential for fusion to become a vital part of the future global energy mix.
Digging deeper into the current market structure, it’s clear that fusion energy is gaining serious traction. The dominance of magnetic confinement methods, particularly in tokamak designs, shows strong industry confidence in this approach. Meanwhile, D-T fuel continues to lead, emphasizing the reliance on proven and efficient fuel cycles. This alignment suggests that the market is heavily investing in technologies with a realistic path to commercialization.
The fusion energy market is projected to nearly double in size by 2034.
Magnetic confinement systems lead with more than 56% share of the market.
Deuterium-tritium fuel remains the dominant choice, holding about 63.5% share.
The industry is growing at a steady CAGR of 6.2% from 2025 to 2034.
 Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/global-fusion-energy-market/free-sample/
Drivers
Fusion energy is gaining momentum as nations push for cleaner, more reliable power sources. Governments are backing large-scale research and development, while private firms invest in fusion startups and infrastructure. Technological breakthroughs in confinement and plasma control are moving fusion closer to viability. Additionally, the growing demand for sustainable base-load power is reinforcing the urgency to commercialize fusion systems.
Opportunities
There is strong potential to scale magnetic confinement reactors from experimental setups to utility-scale power plants. Innovations in fuel types such as alternatives to D-T could open safer and more efficient pathways. Companies working on supporting technologies like superconducting magnets and heat management are also finding new business avenues. International collaborations are fostering knowledge sharing, speeding up development cycles. These factors together present a broad landscape of growth and innovation for fusion stakeholders.
Restraints
High capital investment continues to be a major hurdle for commercial deployment. Fusion reactors involve complex designs that require advanced materials, precision engineering, and years of development. Regulatory frameworks specific to fusion are still under formation, which slows down approvals and deployment. Also, the return on investment is long-term, which can discourage risk-averse investors and governments from moving quickly.
Trends
Magnetic confinement is being widely adopted as the industry standard for fusion development. The D-T reaction remains the most researched and commercially promising fuel cycle. There’s a noticeable shift from experimental setups toward pilot and demonstration-scale plants. Material innovations, particularly in superconductors and heat-resistant alloys, are supporting system stability. Collaborations between nations and between public and private sectors are becoming more strategic and widespread.
| No comments yet. Be the first. |