
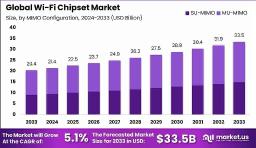
The Global Wi-Fi Chipset Market, valued at USD 20.4 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 33.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.1%, driven by escalating demand for high-speed connectivity and IoT proliferation. Wi-Fi chipsets enable seamless wireless communication across consumer electronics, enterprise, and industrial applications. This market’s growth underscores its critical role in digital transformation. By leveraging advanced MIMO configurations and next-generation protocols, the industry addresses connectivity demands, fostering innovation in a technology-driven global ecosystem amid rising needs for robust, high-performance wireless solutions.
Market growth from USD 20.4 billion (2023) to USD 33.5 billion (2033), CAGR 5.1%.
MU-MIMO dominates configurations with 55% share.
5 GHz band leads with 60% share.
Wi-Fi 6 protocol holds 40% share.
Consumer electronics dominate applications with 45% share.
High costs and compatibility issues are key restraints.
Multi-User MIMO (MU-MIMO) dominates with a 55% share in 2023, driven by its ability to handle multiple devices, enhancing network efficiency. Single-User MIMO (SU-MIMO) grows steadily, supporting legacy systems. Advanced MIMO configurations expand, improving throughput and reliability for high-density environments like enterprises and public spaces.
The 5 GHz band leads with a 60% share, favored for higher speeds and reduced interference. The 2.4 GHz band grows steadily, supporting IoT devices with better range. Tri-band and 6 GHz bands expand, addressing next-generation Wi-Fi needs for ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity in dense networks.
Wi-Fi 6 dominates with a 40% share, driven by enhanced speed and efficiency for IoT and enterprise applications. Wi-Fi 5 grows steadily, supporting legacy devices. Wi-Fi 6E and emerging Wi-Fi 7 protocols expand, offering higher bandwidth and lower latency, catering to advanced connectivity demands across industries.
Consumer electronics dominate with a 45% share, driven by smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices. Enterprise applications grow rapidly, leveraging chipsets for robust network infrastructure. Industrial and automotive sectors expand, adopting Wi-Fi for automation and connected vehicles, broadening market applications across diverse fields.
By MIMO Configuration: MU-MIMO (55% share), SU-MIMO, Others.
By Band: 5 GHz (60% share), 2.4 GHz, Tri-Band, 6 GHz.
By Protocol: Wi-Fi 6 (40% share), Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6E, Wi-Fi 7, Others.
By Application: Consumer Electronics (45% share), Enterprise, Industrial, Automotive, Others.
By Region: North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Latin America, Middle East & Africa.
High development costs (USD 100,000–2 million for advanced chipsets) and compatibility issues with legacy systems hinder adoption. Spectrum congestion and regulatory restrictions challenge scalability. Limited expertise in next-generation protocols like Wi-Fi 7 restricts growth, particularly for SMEs in emerging markets with constrained infrastructure.
Strengths: Advanced MU-MIMO, high consumer electronics adoption, Wi-Fi 6/6E integration.
Weaknesses: High costs, compatibility issues, spectrum congestion.
Opportunities: Asia-Pacific growth, IoT expansion, Wi-Fi 7 adoption.
Threats: Regulatory restrictions, competition from 5G, economic constraints. Growth relies on cost-effective, compatible solutions.
In 2023, 50% of Wi-Fi chipsets adopted Wi-Fi 6, enhancing IoT connectivity. 6 GHz band usage grew 15%, supporting high-speed applications. Partnerships in enterprise networking drove innovation. Asia-Pacific’s 6% CAGR reflects IoT growth. Advanced chipsets saved USD 150 million via optimized network efficiency in 2023.
Leading players focus on Wi-Fi 6/6E chipsets for consumer and enterprise applications. Strategic partnerships with IoT and automotive sectors drive innovation. R&D investments and acquisitions expand market reach, fostering a competitive ecosystem tailored to diverse Wi-Fi chipset needs across industries.
The Global Wi-Fi Chipset Market is poised for steady growth, driven by Wi-Fi 6/6E and IoT advancements. Despite cost and compatibility challenges, opportunities in Asia-Pacific and emerging protocols ensure progress. Key players’ innovations will redefine connectivity efficiency by 2033.
| No comments yet. Be the first. |