Blogs
在台灣的電子霧化產品市場中,悅刻電子菸(RELX)一直是消費者心中的首選品牌之一。憑藉創新的霧化技術與多樣的口味選擇,RELX 已成功將傳統吸菸者轉化為更健康、更時尚的使用者。

隨著需求提升,電子菸線上購買成為趨勢,不僅方便,也能第一時間掌握新品上市資訊。
談到 RELX,不得不提它的多代產品更新,其中第六代推出後,獲得市場極大關注。電子菸 relx 不僅重視外觀設計,更在煙彈體驗上進行了優化,讓使用者在口感與順暢度上獲得雙重滿足。
隨著新一代霧化技術成熟,relx 6代煙彈 成為眾多使用者期待的焦點。它延續 RELX 系列穩定的氣流結構,並進一步減少漏油情況,提升整體耐用性。特別是對於長時間使用者而言,第六代煙彈能提供更均勻的霧化效果。

如果你正在考慮升級設備,那麼 悅刻六代煙彈 絕對值得嘗試。與四代及五代主機兼容的設計,讓舊用戶無須擔心浪費手中設備,直接享受升級後的口感體驗。更令人期待的是,官方持續推出多樣化的口味選擇,讓使用者根據喜好自由挑選。
在眾多新口味中,【金桔百香果】 全新現貨悅刻infinity 2六代煙彈(煙彈x1)(通用Relx 4, 5代主機) 成為近期話題焦點。清新的金桔與酸甜的百香果結合,帶來濃郁而不膩的風味,非常適合喜歡果香口感的用戶。其在夏季尤其受歡迎,不僅清爽解膩,還能展現 RELX 對於創新口味的持續追求。
值得一提的是,電子菸市場競爭激烈,除了 RELX 之外,還有許多新興品牌嶄露頭角。例如,LANA電子菸:台灣市場的潮流選擇 一文中介紹的 LANA 品牌,憑藉獨特設計與多元口味,也成為年輕族群的熱門選擇。如果你想全面了解不同品牌優勢,這篇文章將帶來完整的比較與分析。

整體來說,無論是長期 RELX 用戶,還是正打算入門電子菸的新手,第六代產品都展現了高度誠意。從外型設計到口味選擇,甚至到與舊主機兼容的細節,皆充分體現品牌對使用者體驗的重視。而線上通路的普及,則讓消費者能以最快速度入手心儀的煙彈。
未來,隨著電子霧化產品市場的持續擴展,RELX 勢必將持續推出更多驚喜。不論你偏愛經典還是追求創新,悅刻的六代系列都值得一試。
relx 電子菸
relx
悅刻
悅刻電子菸
電子菸 relx
電子菸線上購買
悅客電子菸
relex
悅克
relx電子煙
瑞克電子菸
悅刻主機
relx 主機
relx 電子菸台灣
電子菸主機
電子霧化器
電子菸價錢
悅刻煙彈
relx 煙彈口味
relx 煙彈
relx 煙彈口味推薦
悅刻煙彈口味
煙彈 relx
relx 煙彈台灣
電子菸口味
菸彈電子菸
銳克煙彈
煙彈
菸彈
煙蛋
電子菸價格
煙彈口味
電子菸菸彈
電子菸購買
relx 1 代
relx 5代
悅刻五代
relx 6代
悅刻六代
relx 5代主機
悅刻五代主機
relx 6代主機
悅刻六代主機
relx 5代煙彈
悅刻五代煙彈
relx 6代煙彈
悅刻六代煙彈
煙彈
悅刻煙彈
菸彈
relx煙彈口味
relx煙彈
煙彈
煙彈 relx
電子菸菸彈
relex
relx 電子菸口味
悅克
電子菸 relx
relx 電子菸價格
relx 電子菸台灣
電子菸主機
悅客電子菸
nike air max 97
nike ambush
nike dunk low灰白
nike p 6000
nike shoes
nike tw
nike 休閒 鞋
nike 員 購 店
nike 涼鞋
nike 白 鞋
sacai x nike vaporwaffle
yeezy 700
愛 迪 達 鞋子 2019 新款
椰子 鞋
nike air max 90
nike air zoom
nike court
nike court borough low 2
nike pegasus
nike tc7900
nike vomero
nike 氣墊 鞋
nike 籃球
耐 吉 鞋
yeezy 500
adidas 4d
adidas boost
ambush nike
nike 97
nike air force 女
nike air max 270
nike blazer
nike force
nike react
nike store
Introduction
If you're hoping to go further than gamble on Kheloyar - you would like to make money, you need an action plan. This guide will provide you with five tips to help you stretch your cash-flow, minimize losses, and take better bets. Learn how to choose the right value markets, control risk, make use of data and secure profits whenever odds are moving your direction.
1: Set Bankroll Rules You Actually Follow
Your bank account is your company's capital. Make sure you protect it.
- Set a stop loss: If you fall 5-10% over the course of a day, you should stop. Avoid tilts and poor choices.
- Scale up or down: The size of the unit should be increased only after the bankroll gains of 20-25 percent and decrease following a drawdown.
The reason it works Fixed units stop the cold streak from sweeping your game and keeps you playing for long enough to allow your edge to be evident.
2: Hunt for Value, Not Hype
- Compare lines: Look at different marketplaces with Kheloyar App . When Team A's value is a market with a value of +140 but +155 in a different market across possibilities, you've found additional value.
- Create a basic model to track recent injuries, forms or travel statistics. A simple spreadsheet that calculates win probability can help you identify mispriced odds.
- Place a bet on a cushion. Aim at a 5-10% perceptual edge before placing a wager.
3: Specialize in One Market to Gain an Edge
Generalists try to chase everything, but they fall prey their way to juice. Specialists understand the quirks.
- Select a niche. Two or three leagues or a market that is specific, such as totals or props for players.
- Monitor micro-trends by playing back-to-back games, a short break, traveling distance, speed and even weather.
- Keep a journal: Your reasoning and your results. When you place more than 50 bets and patterns emerge.
Results: Your reading skills improve as variance is smoothed out and you transform your information into predictable results.
4: Make use of Promotions and Bonuses in conjunction using a plan
Promotions can shift the numbers for you if you choose to use them correctly.
- Learn the definitions: Concentrate on deals with a low rollover and market segments you are already familiar with.
- Low-variance bets: If you are clearing rollovers, select the most tense lines or double-chance outcomes to safeguard your promotional value.
- Stack value: Match the opportunity to make more money with a line that you already enjoy, not the opposite.
Pro tip: Track the promo profits separately to determine the real return on investment from bonuses as opposed to. regular bets.
5: Cash-Out and Hedge at the Right Moments
The odds of winning bets could fail. Make sure you are in the pocket of profits as the market shifts to your advantage.
- Make a pre-plan for exits: Determine prior to the start of the game the time you'll be able to hedge (e.g. in the event that the odds on live games decrease by 25-30 percent).
- Partial hedge: Secure the other side by putting in less of a stake to earn an income base while maintaining the upside.
- Avoid emergency exits: Only cash out when your anticipated value increases due to a reduction in risk, not just in order to "feel safe."
Quick Summary Table
|
Hack |
What It Does |
How to Apply |
Risk Level |
|
Bankroll Rules |
Limits the loss, prolongs the duration of |
Size of the fixed unit and stop-loss |
Low |
|
Value Hunting |
Finds odds that are undervalued |
Compare odds, target 5-10% edge |
Medium |
|
Market Specialization |
Gains an edge in a particular area |
Track One or two sports or leagues |
Low |
|
Smart Bonuses |
Turns promos into profit |
Rollovers or low-variance bets |
Low-Medium |
|
Cash-Out & Hedging |
Locks profit, caps downside |
Partial hedge in key points |
Medium |
FAQs
Q1 Is there a daily betting limit?
A: Quality beats quantity. A bet that is well-studied and two to five times more profitable are more profitable than chasing the action.
Q2: What happens if I have a losing streak that isn't so great?
A: Cut the unit size. Follow this plan. Examine your logs to find leaks.
Q3: Is it worth the cost?
Be careful with them. If you decide to play them, make sure your legs are correlated with your research, and not hope.
Q4: What do I need to make my bankroll?
A: Put money into a fund you are able to afford to take on. Begin by placing at a minimum of 50-100 bets the size you prefer for your unit.
Q5: Do cash-outs hurt profits over the long run?
A: Don't use it when the market shifts to your advantage and you're increasing the value you expect to earn. Do not make emotional payouts.
Conclusion
Profits that are sustainable on Kheloyar depend on discipline and not luck. Make sure you have strict bankroll guidelines, be focused on value, focus on specific areas, utilize promotions with a purpose and hedge when numbers suggest it. Begin small, keep track of everything and then let your edge build over time.
Read More - https://kheloyar2.com/greyhound-racing-7-expert-tips-to-improve-your-wins/
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market Forecast 2025–2030: Trends, Share, Growth Drivers & Key Players
By dannykinggt, 2025-08-18
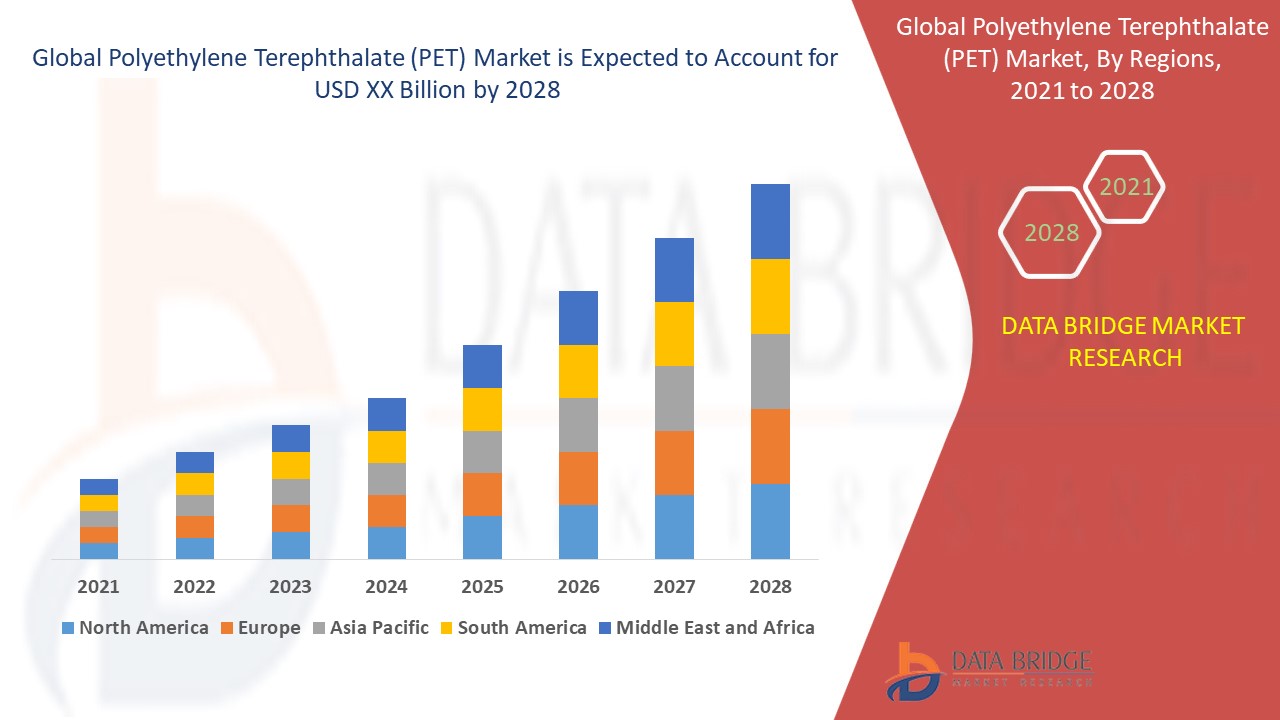 "Market Trends Shaping Executive Summary Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market Size and Share
"Market Trends Shaping Executive Summary Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market Size and Share
The polyethylene terephthalate (PET) market size was valued at USD 26.99 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 46.79 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 7.12% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2032
The Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market report puts light on the change in the market which is taking place due to the moves of key players and brands such as product launches, joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions that in turn modifies the view of the global face of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market industry. This market report takes into account myriad of aspects of the market analysis which today’s businesses call for. To make the report outstanding, most up-to-date and advanced tools and techniques are used so that client achieves maximum benefits. The Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market report also includes the market drivers and market restraints that are derived from SWOT analysis.
This Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market report helps businesses thrive in the market by providing them with a lot of insights about the market and the Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market industry. The key factors here include industry outlook with respect to critical success factors (CSFs), industry dynamics that mainly covers drivers and restraints, market segmentation & value chain analysis, key opportunities, application and technology outlook, regional or geographical insight, country-level analysis, key company profiles, competitive landscape, and company market share analysis. Thus, Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market research report is very important in many ways to grow your business and to be successful.
Unlock detailed insights into the growth path of the Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market. Download full report here:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-polyethylene-terephthalate-pet-market
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Industry Performance Overview
**Segments**
- By Type: The PET market can be segmented based on type into Fiber Grade, Bottle Grade, and Film Grade. Fiber grade PET is primarily used in the textile industry for manufacturing fibers and fabrics. Bottle grade PET is commonly used in the production of plastic bottles for packaging beverages, personal care products, and household items. Film grade PET is used in the manufacturing of flexible packaging materials such as films and sheets.
- By Application: The market can also be segmented by application, including Packaging, Automotive, Electronics, Textiles, and Others. Packaging is the largest application segment for PET, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and recyclable packaging solutions. The automotive industry is utilizing PET for various components due to its lightweight and durable properties. In the electronics sector, PET is used for manufacturing electronic components and devices. The textile industry also utilizes PET for producing synthetic fibers and fabrics.
**Market Players**
- Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited: A leading player in the global PET market, Indorama Ventures is involved in the manufacturing and sale of PET resins for various applications such as packaging, textiles, and beverages.
- DAK Americas: DAK Americas is a key player in the PET market, offering a range of PET resins for different end-use industries including packaging, automotive, and consumer goods.
- Far Eastern New Century Corporation: Far Eastern New Century Corporation is a prominent manufacturer of PET products, catering to industries such as textiles, packaging, and electronics.
- SABIC: SABIC is a major player in the PET market, providing high-quality PET resins for diverse applications including packaging, automotive, and construction.
- M&G Chemicals: M&G Chemicals is a well-established company in the PET market, focusing on the production of PET resins for packaging, textiles, and other applications.
For more detailed insights and market analysis on the Global Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market, visit: The global polyethylene terephthalate (PET) market is witnessing significant growth and innovation across various segments and applications. One emerging trend in the market is the increasing focus on sustainable and recyclable packaging solutions, driving the demand for PET materials in the packaging industry. With growing environmental concerns and regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly materials, PET is becoming a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and offer more sustainable packaging options to consumers.
Another key factor influencing the PET market is the rise in demand for lightweight and durable materials in industries such as automotive and electronics. PET's properties make it a suitable material for automotive components and electronic devices, where factors like strength, flexibility, and thermal stability are crucial. As these industries continue to innovate and expand, the demand for PET resins is expected to grow, creating opportunities for market players to introduce new products and technologies to meet evolving industry requirements.
Moreover, the textile industry remains a significant consumer of PET materials, particularly in the production of synthetic fibers and fabrics. PET's versatility and affordability make it a popular choice for textile manufacturers looking to enhance the performance and sustainability of their products. With the increasing emphasis on sustainable fashion and the circular economy, PET-based textiles are gaining traction as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional materials.
In terms of market players, companies like Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited, DAK Americas, Far Eastern New Century Corporation, SABIC, and M&G Chemicals are driving innovation and growth in the global PET market. These key players are investing in research and development initiatives to develop new PET formulations, expand their product portfolios, and cater to a wide range of end-use industries. By leveraging their expertise and market presence, these companies are contributing to the overall growth and competitiveness of the PET market on a global scale.
In conclusion, the global polyethylene terephthalate (PET) market is characterized by evolving trends, increased demand across diverse applications, and strong competition among market players. With a focus on sustainability, innovation, and market expansion, the PET industry is poised for continued growth and development in the coming years. As consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly products and industries seek more efficient and cost-effective materials, PET is expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of packaging, automotive, textiles, and other sectors.The global polyethylene terephthalate (PET) market continues to witness significant growth and evolution, driven by various factors influencing its diverse segments and applications. One of the notable trends impacting the market is the increasing emphasis on sustainability and recyclability in packaging solutions. As consumers and regulators prioritize eco-friendly materials, PET is gaining traction as a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to reduce environmental impact and offer sustainable packaging options. This shifting preference towards sustainable packaging is reshaping the market landscape and presenting opportunities for PET producers to innovate and meet the evolving demands of the industry.
Another pivotal driver of the PET market is the surge in demand for lightweight and durable materials across industries such as automotive and electronics. With its inherent properties like strength, flexibility, and thermal stability, PET is well-suited for various applications in these sectors. As automotive and electronics manufacturers increasingly adopt PET for components and devices, the market for PET resins is forecasted to expand further. This trend signifies a growing reliance on PET as a material of choice for industries prioritizing performance, efficiency, and sustainability in their products.
Furthermore, the textile industry remains a significant consumer of PET materials, particularly in the production of synthetic fibers and fabrics. The versatility and cost-effectiveness of PET make it an attractive option for textile manufacturers looking to enhance the sustainability and performance of their offerings. With the escalating focus on sustainable fashion and the circular economy, PET-based textiles are gaining popularity as an eco-conscious alternative to conventional materials. This trend reflects the textile industry's shift towards more sustainable practices and materials, driving the demand for PET in textile applications.
In terms of market players, key companies such as Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited, DAK Americas, Far Eastern New Century Corporation, SABIC, and M&G Chemicals are at the forefront of driving innovation and growth in the global PET market. Through investments in research and development, product diversification, and industry partnerships, these players are spearheading advancements in PET technology and applications across multiple sectors. Their strategic initiatives are not only contributing to market expansion but also fostering competition and driving the overall progress of the PET industry on a global scale.
In conclusion, the global PET market is poised for continued growth and development, propelled by sustainability drivers, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. As market players continue to innovate and collaborate to meet the demands of a changing industry landscape, PET is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of packaging, automotive, textiles, and other key sectors. The dynamic nature of the PET market presents opportunities for companies to differentiate themselves through sustainable practices, product innovation, and strategic partnerships, ensuring a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market environment.
Check out detailed stats on company market coverage
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-polyethylene-terephthalate-pet-market/companies
In-Depth Market Research Questions for Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market Studies
- What revenue figures define the current Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market?
- What are the near-term and long-term growth rates expected in Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market?
- What are the dominant segments in the Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market overview?
- Which companies are covered in the competitor analysis for Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market?
- What countries are considered major contributors for Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market?
- Who are the high-growth players in the Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market?
Browse More Reports:
Global Bottled Water Market
Global Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Market
Global Industrial Valves Market
Global Vending Machine Market
Global Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Market
Global Carrageenan Market
Global Individual Quick Freeze (IQF) Fruits Market
Global Diving Tourism Market
Global Non-Invasive Glucose Meter Market
Middle East Electric Vehicle Market
Global Denosumab Market
Global Dimethyl Ether Market
Global Fat Powder Market
Global Luxury Jewellery Market
Global Predictive Maintenance Market
Middle East and Africa Lymphedema Treatment Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com
"
Where to Watch Sports and Movie Streaming Your Favorite Content Online
By watchtostreams, 2025-08-18
In the rapidly evolving digital age, live streaming has emerged as a game-changer in the way people consume content. It allows real-time broadcast of events, games, shows, and user-generated content to a global audience through the internet. Whether it’s watching your favorite sports match, attending a virtual concert, or participating in a business webinar, live streaming has made it all accessible with just a click. At the forefront of this digital transformation is WatchToStreams, a platform dedicated to delivering high-quality, seamless live streaming experiences across various genres and interests.
Live streaming offers a unique sense of immediacy and interaction that traditional media lacks. Unlike pre-recorded videos, live content encourages audience engagement through live chats, real-time reactions, and instant feedback. This real-time interaction creates a deeper connection between content creators and their audiences, whether they are influencers, gamers, artists, or businesses. WatchToStreams capitalizes on this by providing creators with tools to reach their viewers instantly while ensuring high-definition, buffer-free viewing experiences for users.
One of the key advantages of live streaming is its accessibility. With a stable internet connection and a smart device, anyone can stream or watch live content from anywhere in the world. WatchToStreams understands this global need and ensures compatibility across multiple devices—smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart TVs—making it easy for users to tune into their favorite live events on the go.
Moreover, live streaming isn’t just for entertainment. Businesses use live streaming for product launches, virtual meetings, and customer interaction. Educational institutions conduct online classes, webinars, and tutorials. Fitness instructors run live workout sessions. Religious organizations broadcast sermons and spiritual events. The possibilities are endless, and WatchToStreams provides a reliable platform for each of these sectors to engage with their audience effectively.
From a technical perspective, WatchToStreams focuses on scalability, low latency, and user-friendly interfaces. These technical elements are crucial to maintaining quality and ensuring uninterrupted broadcasts. The company employs robust servers and cutting-edge streaming technologies to support large viewership without compromising on quality.
Monetization is another important aspect of live streaming, and WatchToStreams offers content creators various options such as ad integration, pay-per-view events, and subscription-based models. This empowers creators and businesses to generate revenue while delivering valuable content to their audience.
In today’s competitive digital world, visibility and discoverability are key. That’s why WatchToStreams also emphasizes SEO-friendly tagging, personalized recommendations, and social sharing features to help content reach the right audience. Whether you’re a new creator or an established brand, the platform ensures your live streams gain the attention they deserve.
In conclusion, live streaming is no longer a trend—it’s a vital part of modern digital communication and entertainment. With the increasing demand for real-time content, platforms like WatchToStreams are playing a crucial role in shaping the future of media. By combining advanced technology with user-centric features, WatchToStreams is not just keeping up with the times—it’s leading the way.
Upgrading technology often leaves behind outdated or damaged motherboards and printed circuit boards (PCBs). Instead of letting them clutter your space or harm the environment, you can turn them into profit with money for motherboards. At WeeeSouth, we specialize in offering cash for motherboards, cash for PCBs, and cash for circuit boards, providing fast quotes, competitive prices, and eco-friendly disposal. Whether you’re an individual, business, or recycler, our motherboard buyers and PCB buyers make it easy to earn money for circuit boards while ensuring responsible motherboard recycling and PCB recycling. This guide covers how to sell your electronics, the benefits of circuit board recycling, and why WeeeSouth is your top choice for motherboard disposal and PCB disposal.
Why You Should Sell Motherboards and PCBs for Cash
Motherboards and PCBs contain valuable materials like gold, copper, and silver, which can be recycled to create new electronics. Selling these components for money for motherboards or money for PCBs not only puts cash in your pocket but also prevents e-waste. Improper motherboard disposal or circuit board disposal can release toxic substances like lead or mercury into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. By choosing circuit board recycling, you support sustainability and a circular economy.
WeeeSouth’s motherboard buyers and circuit board buyers offer a seamless process to sell your electronics. We accept used, damaged, or obsolete motherboards and PCBs, ensuring you get cash for circuit boards while contributing to eco-friendly practices.
How to Earn Money for Motherboards and PCBs
Getting money for motherboards and cash for PCBs with WeeeSouth is straightforward. Follow these steps to sell your electronics:
- Collect Your Components: Gather motherboards, PCBs, or circuit boards from computers, servers, or other devices, regardless of condition.
- Get a Fast Quote: Contact us at call 0333 533 0366 for a quick, no-obligation quote. Send details or photos of your items, and our PCB buyers will provide a fair offer based on market value and condition.
- Arrange Collection or Drop-Off: Visit us at 23 Benson Close, Reading, RG2 7LP, or schedule a free pickup during our hours (Monday – Sunday, 9am to 6pm) for motherboard recycling and PCB recycling.
- Receive Payment: After evaluation, get money for circuit boards quickly via your preferred payment method.
Our circuit board buyers ensure transparency, offering competitive rates for all types of motherboards and PCBs.
Benefits of Selling to WeeeSouth
Choosing WeeeSouth for cash for motherboards and cash for PCBs comes with numerous advantages:
- Fair Pricing: We provide market-competitive rates, ensuring you maximize money for motherboards and money for PCBs.
- Eco-Friendly Process: Our circuit board recycling and PCB disposal methods comply with environmental regulations, reducing e-waste.
- Convenient Service: Free collection and fast payments make selling your electronics hassle-free. Contact us at 0333 533 0366 or visit 23 Benson Close, Reading, RG2 7LP.
- Expertise: Our team specializes in evaluating all types of circuit boards, from legacy motherboards to modern PCBs, for accurate valuations.
Whether you’re looking to recycle motherboards or dispose of circuit boards, WeeeSouth combines profitability with sustainability.
Who Can Sell Motherboards and PCBs?
Our services cater to a diverse range of customers looking to earn money for motherboards and cash for circuit boards:
- Individuals: Turn old computers or electronics into cash with motherboard recycling. Clear out your space while earning money for circuit boards.
- Businesses: IT firms, repair shops, and manufacturers can sell bulk motherboards and PCBs for cash for PCBs, ensuring compliance with disposal regulations.
- Recyclers and Resellers: Those with large quantities of circuit boards can partner with our circuit board buyers for consistent payouts and reliable PCB recycling.
No matter your needs, WeeeSouth makes motherboard disposal and PCB disposal profitable and responsible. Reach out to get started.
The Importance of Responsible Circuit Board Disposal
Improper circuit board disposal or motherboard disposal can lead to environmental pollution and data security risks. Motherboards may contain sensitive data in memory chips, requiring secure destruction to prevent breaches. By choosing motherboard recycling or PCB recycling, you ensure:
- Data Security: We use certified data wiping or physical destruction to protect sensitive information.
- Environmental Safety: Our circuit board recycling process extracts valuable materials and safely disposes of hazardous substances.
- Regulatory Compliance: We adhere to WEEE and other environmental standards for responsible PCB disposal.
Selling to WeeeSouth means earning money for motherboards while supporting a greener planet.
Frequently Asked Questions About Money for Motherboards
How Can I Get Money for Motherboards?
Contact WeeeSouth at 0333 533 0366 for a free quote. Provide details or images of your motherboards, and our motherboard buyers will offer a fair price based on condition and market value.
What Types of PCBs Are Accepted?
We buy all types of PCBs, including those from computers, servers, industrial equipment, and medical devices. Whether damaged or obsolete, you can earn cash for PCBs.
Is Circuit Board Recycling Environmentally Friendly?
Yes, our circuit board recycling process ensures hazardous materials are safely handled, and reusable components are repurposed, minimizing environmental impact.
How Quickly Can I Get Cash for Circuit Boards?
Our process is fast. Receive a quote within hours, arrange pickup or drop-off at 23 Benson Close, Reading, RG2 7LP (Monday – Sunday, 9am to 6pm), and get money for circuit boards upon evaluation, often within days.
Why Choose WeeeSouth for Motherboard and PCB Recycling?
WeeeSouth is a trusted leader in motherboard disposal and PCB recycling, offering expertise, transparency, and customer-focused service. Here’s why we’re the best choice for cash for motherboards and cash for PCBs:
- Transparent Pricing: Clear, competitive quotes with no hidden fees for money for motherboards or money for PCBs.
- Convenient Logistics: Free collection services or drop-off at 23 Benson Close, Reading, RG2 7LP simplify motherboard disposal and PCB disposal.
- Sustainable Practices: Our circuit board recycling supports a circular economy by reusing valuable materials.
- Customer Satisfaction: We prioritize your needs, offering personalized service for individuals and businesses.
Act Now: Turn Your Motherboards and PCBs into Cash
Don’t let old motherboards and PCBs go to waste. With WeeeSouth, you can earn money for motherboards, cash for PCBs, and money for circuit boards while supporting eco-friendly practices. Our motherboard buyers and PCB buyers offer fast quotes, fair prices, and convenient services for all types of electronics, whether used, damaged, or obsolete.
Contact WeeeSouth today at 0333 533 0366 to request a quote and schedule a pickup or visit us at 23 Benson Close, Reading, RG2 7LP (Monday – Sunday, 9am to 6pm). Join thousands of satisfied customers who’ve turned their electronics into profit with our circuit board recycling services. Act now to earn cash for motherboards and contribute to a sustainable future!
History is more than just a study of past events—it's a rich tapestry that connects civilizations, cultures, and human experiences across time. However, for many students, history assignments can be challenging due to the complexity of timelines, detailed analysis, and critical thinking they demand. Whether you're struggling with ancient civilizations, modern political history, or thematic essays, MyAssignmentsPro offers accurate and timely History Assignment Help designed to make your academic journey smoother and more successful.
Why History Assignments Can Be Challenging
History is a subject that requires not only memorization of dates and facts but also deep interpretation, contextual understanding, and analytical writing. Here are some common challenges students face:
- Vast content: History spans thousands of years and includes countless events, ideologies, movements, and figures.
- Complex essay questions: Assignments often demand critical analysis, comparison, and historical argumentation.
- Proper referencing: Using citations correctly (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) is crucial when using historical sources.
- Time management: With tight academic schedules, students often struggle to dedicate enough time to detailed historical research.
If these issues sound familiar, you're not alone. That’s where MyAssignmentsPro steps in to help you manage the workload and excel.
What Is MyAssignmentsPro?
MyAssignmentsPro is a professional academic assistance platform offering top-quality support for students across various disciplines. One of its standout services is History Assignment Help, provided by a team of experienced historians, educators, and academic writers. Whether it’s an essay, research paper, case study, or dissertation, the experts at MyAssignmentsPro can assist you at every step—from research to final proofreading.
Features of Our History Assignment Help
Here’s why thousands of students trust MyAssignmentsPro for their history assignments:
✅ Accurate and In-Depth Content
Our team is composed of highly qualified history experts who are well-versed in both global and regional histories. They understand historical contexts, primary and secondary sources, and academic conventions. This ensures that every assignment you receive is:
- Factually correct and well-researched
- Contextually appropriate and historically accurate
- Reflective of critical thinking and scholarly insights
✅ Timely Delivery, Every Time
Missed deadlines can hurt your academic performance. That’s why our team works round-the-clock to ensure that every history assignment is delivered on or before your deadline. Whether you need a quick turnaround in 24 hours or a detailed paper in a week, we’ve got your back.
✅ Customized Solutions
Every assignment is different. At MyAssignmentsPro, we offer tailored assistance that aligns with your specific instructions, grading rubric, academic level, and formatting preferences. No generic or recycled content—just original work that meets your needs.
✅ 100% Plagiarism-Free Work
Academic integrity is one of our core values. All our history assignments are written from scratch, and we use advanced plagiarism-detection tools to ensure originality. You’ll also receive a free plagiarism report with your assignment upon request.
✅ Expert Support Across All Historical Topics
From ancient civilizations to modern global conflicts, our experts cover a wide range of topics, including but not limited to:
- World War I & II
- Cold War and Post-Cold War era
- American Revolution and Civil Rights Movement
- European Renaissance and Enlightenment
- Colonialism and Decolonization
- Indian, Chinese, and Middle Eastern history
- Political ideologies and revolutions
- Gender, race, and class in historical contexts
Types of History Assignments We Handle
MyAssignmentsPro can help you with all kinds of history tasks, including:
- Essays and argumentative papers
- Research papers
- Case studies
- Biographical assignments
- Document-based questions (DBQs)
- Annotated bibliographies
- Comparative historical analysis
- Presentations and timelines
- Dissertations and thesis writing
Whether it’s a high school essay or a postgraduate thesis, we have the expertise to deliver high-quality work.
Benefits of Choosing MyAssignmentsPro
Here are some of the reasons students around the world choose us for their history assignment needs:
📌 24/7 Customer Support
We understand that assignment emergencies can happen anytime. Our support team is available 24/7 via chat, email, or phone to address any queries or concerns.
📌 Affordable Pricing
We offer student-friendly rates and special discounts without compromising on quality. Transparent pricing with no hidden charges.
📌 Free Revisions
Not satisfied with the first draft? No worries! We offer free unlimited revisions until you’re completely happy with the result.
📌 Confidentiality Guaranteed
Your personal information and assignment details are 100% confidential. We follow strict privacy policies to protect your identity and data.
How It Works
Getting history assignment help from MyAssignmentsPro is easy and hassle-free. Just follow these steps:
- Submit Your Assignment Details
Fill out a simple form with your topic, deadline, word count, and special instructions. - Get a Quote
Receive an affordable price estimate based on your assignment requirements. - Make Payment
Choose from secure payment options to confirm your order. - Assignment Delivered on Time
Receive your completed assignment well before the deadline, ready to be submitted. - Request Revisions (If Needed)
Review the work and request revisions if anything needs to be updated—free of cost.
Final Thoughts
Don’t let complex history assignments weigh you down. With MyAssignmentsPro, you get accurate, well-researched, and timely academic assistance tailored to your needs. Whether you're running out of time, struggling with the content, or simply want to boost your grades, our team of qualified history experts is here to help.
Take control of your academic success—get in touch with MyAssignmentsPro today and experience stress-free learning like never before!
📞 Contact Us
Ready to get started? Reach out to us now!
🌐 Website: www.myassignmentspro.com
💬 Live Chat: Available 24/7 on our website
HR Payroll Software Market Outlook 2021–2031 with Trends and Growth Opportunities
By Pranita32, 2025-08-18
According to a new report published by Allied Market Research, titled, “HR Payroll Software," The hr payroll software market was valued at $23.55 billion in 2021, and is estimated to reach $55.69 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 9.16% from 2022 to 2031.
The HR payroll software streamlines end-to-end payroll process & reduces the workload of staff members or employees. It generates various types of insightful payroll & employees or staff performance related reports within few minutes. The integration of payroll and HR software enable managers or staff members to access all essential information from a single dash-board. Combining the payroll process with the best of HR functionality enhances efficiency in managing employee data. Moreover, HR payroll software saves time & money and reduces number of errors, which provide lucrative growth opportunities for the market. Furthermore, rise in investments in the industry such as BFSI, healthcare, & manufacturing sector and increase in deployment of cloud-based HR payroll software further propel the growth of the market during the forecast period.
On the basis of organization size, the large enterprises dominated the overall HR payroll software industry in 2021 and is expected to continue this trend during the forecast period. There is an increase in the adoption of HR payroll software in large enterprises to operate a lean payroll and tax filling service. Also, as organizations expand, this balancing act becomes even more difficult. Furthermore, large enterprises are integrating their large volume of data in the cloud to augment their speed, accuracy, and value chain scalability, which is opportunistic for the market. However, the SME’s is expected to witness the highest HR payroll software market growth in the upcoming year. The adoption of HR payroll software is expected to increase to optimize the business capabilities of small & medium sized enterprises. Moreover, continuous rise in number of government initiatives through various digital SME campaigns throughout the world fuel the growth of the market.
Depending on industry vertical, the IT & telecom sector dominated the HR Payroll Software Market Share in 2021 and is expected to continue this trend during the HR Payroll Software Market Forecast period. Increase adoption of HR payroll software in IT & telecom industry to make processes paper-free, more efficient & accurate and save lot of productive hours for the HR management team. In addition, HR and payroll process move towards the digitization and technology initiatives motivated by the global pandemic, provide lucrative growth opportunities for the HR payroll software market in the IT & telecom sector. However, healthcare sector is expected to witness the highest growth in the upcoming year. The HR payroll software is gaining popularity in the healthcare sector, owing to enhanced end to end security with patient data, cost benefits, and improved connectivity benefits that it offers to users. In addition, increase in digitalization and better graphical user interaction further boost the demand for HR Payroll Software Market Share in the healthcare sector.
The HR Payroll Software Industry was valued at $25.30 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach $55.69 billion by 2031, registering a CAGR of 9.2%. The current estimation of 2031 is projected to be higher than pre-COVID-19 estimates. Governments and businesses are increasingly asking employees to work from home or are shifting work to employees in less affected areas to maintain business continuity during the pandemic. However, the situation has accelerated the adoption of advanced technologies such as AI powered solution, automation, big data, and analytics to control costs while improving the customer experience. Furthermore, organizations may now transform unstructured and semi-structured data into structured and relevant data due to the advent of big data and analytics. This data can be used by HR Payroll System to help enterprises speed up data management, process & analyze data, and improve the efficiency of business processes. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI) integration aids in the extraction of new insights from existing data in order to improve credit decisions, financial risk management, and consumer experience via intelligent chatbots. As a result, the growth in requirement to modernize HR and payroll operations is expected to propel market growth globally during the forecast period. For instance, in May 2020; the cloud-based HR Payroll System provider, Paylocity introduced the product features for the automation of the “IRS Form 7200” to advance payment of employer credits, along with product mobilization to help clients recruit, rehire and engage their workforce during the COVID-19 crisis.
KEY FINDINGS OF THE STUDY
- By component, the software segment dominated the HR Payroll Software Industry in 2021. However, the services segment is expected to exhibit significant growth during the forecast period.
- On the basis of deployment mode, the on-premise segment dominated the HR payroll software market in 2021; However, the cloud segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period.
- Depending on organizational size, the large enterprises generated the highest revenue in 2021. However, the SMEs segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the near future.
- Depending on industry vertical, the IT & telecom industry generated the highest revenue in 2021. However, the healthcare industry is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the near future.
- Region-wise, the HR Payroll Software Market Size was dominated by North America in 2021. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years.
This report gives an in-depth profile of some key market players in the HR payroll software market, include ADP, LLC, Ascentis Corporation, Cornerstone OnDemand, Inc., Epicore Software, Oracle Corporation, Patriot software, Paycom software Inc., Sage Plc., SAP SE, and SumTotal Systems Inc. This study includes market trends, market analysis, and future estimations to determine the imminent investment pockets.
Market Share Battle: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Industry Key Companies & Growth Strategies
By dannykinggt, 2025-08-18
 "Future of Executive Summary Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market: Size and Share Dynamics
"Future of Executive Summary Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market: Size and Share Dynamics
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the global artificial intelligence (AI) insurtech market which was USD 3,640 million in 2022, is expected to reach USD 35,770 million by 2030, and is expected to undergo a CAGR of 33.06% during the forecast period of 2023 to 2030.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market research report is a sure solution to get market insights with which business can visualize market place clearly and thereby take important decisions for growth of the business. By getting an inspiration from the marketing strategies of rivals, businesses can set up inventive ideas and striking sales targets which in turn make them achieve competitive advantage over its competitors. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market report inspects the market with respect to general market conditions, market improvement, market scenarios, development, cost and profit of the specified market regions, position and comparative pricing between major players.
An influential Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market report conducts study of market drivers, market restraints, opportunities and challenges underneath market overview which provides valuable insights to businesses for taking right moves. This market report is a source of information about Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market industry which puts forth current and upcoming technical and financial details of the industry to 2029. The report is a window to the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market industry which defines properly what market definition, classifications, applications, engagements and market trends are. Moreover, market restraints, brand positioning, and customer behavior, is also studied with which achieving a success in the competitive marketplace is simplified.
Tap into future trends and opportunities shaping the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market. Download the complete report:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-artificial-intelligence-ai-insurtech-market
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market Environment
**Segments**
- On the basis of Component, the Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market can be segmented into Solutions and Services. The Solutions segment includes software tools and platforms that incorporate AI technology to streamline insurance processes. On the other hand, the Services segment comprises consulting, integration, and support services that facilitate the implementation and maintenance of AI-driven solutions in the insurance sector.
- By Application, this market can be categorized into Chatbots, Customer Behavioral Analytics, Claims Management, Personalization, Policy Underwriting, and Fraud Detection. Chatbots are increasingly being adopted by insurance companies to enhance customer service and streamline communication processes. Customer Behavioral Analytics leverages AI algorithms to analyze customer data and provide insights for personalized services. Claims Management involves using AI tools to automate and expedite claims processing. Personalization in the insurance sector is made possible by AI technologies that tailor products and services to individual customer needs. Policy Underwriting is another critical application of AI in insurtech, where automated processes are used to assess risk and determine policy pricing. Lastly, Fraud Detection uses AI-powered algorithms to identify and prevent fraudulent activities within the insurance industry.
- On the basis of End-User, the AI Insurtech Market is segmented into Insurance Companies, Agents & Brokers, and Others. Insurance companies are the primary end-users of AI insurtech solutions, utilizing these technologies to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, and drive innovation in product development and risk management. Agents and brokers also benefit from AI tools that help them automate routine tasks, generate leads, and provide personalized recommendations to clients. Other end-users in the insurtech market include reinsurers, insurtech startups, and third-party service providers that support the insurance industry with AI-driven solutions.
**Market Players**
- Some of the key players in the Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market are IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Amazon Web Services, Inc., Oracle Corporation, Google LLC, SAP SE, Salesforce.com, Inc., Intel Corporation, AntWorks, App Orchid, BIMA, Quantemplate, Relay, Shift Technology, Tractable, etc. These market players are actively investing in research and development to enhance their AI capabilities for the insurance industry.
- Additionally, insurtech startups like Lemonade, PolicyBazaar, and Oscar Health are disrupting the traditional insurance landscape with innovative AI-driven solutions. These players are leveraging technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to transform insurance processes and offer more personalized services to customers.
The Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market is witnessing significant growth and evolution driven by the increasing adoption of AI technologies in the insurance sector. One of the emerging trends in the market is the focus on enhancing customer experience through innovative solutions such as Chatbots, Customer Behavioral Analytics, and Personalization. Insurance companies are leveraging AI-powered tools to provide more personalized services, streamline communication processes, and automate routine tasks. This trend is reshaping the traditional insurance landscape by enabling insurers to better understand customer needs, optimize pricing strategies, and mitigate risks more effectively.
Moreover, the integration of AI in Claims Management and Fraud Detection is revolutionizing how insurance companies process claims and detect fraudulent activities. By automating claims processing and utilizing advanced algorithms for fraud detection, insurers can improve operational efficiency, minimize losses due to fraudulent activities, and enhance overall risk management practices. This increased focus on operational excellence and risk mitigation is driving the demand for AI insurtech solutions among insurance companies, agents, brokers, and other stakeholders in the industry.
Another noteworthy aspect of the market is the growing ecosystem of market players, including both established tech giants like IBM, Microsoft, and Google, as well as emerging insurtech startups such as Lemonade, PolicyBazaar, and Oscar Health. These players are continuously investing in R&D to enhance their AI capabilities and develop innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of the insurance industry. The competition among these market players is driving innovation and fueling the development of cutting-edge AI technologies that are reshaping the insurance landscape.
Furthermore, the shift towards digitalization and the increasing focus on data analytics and predictive modeling are key drivers shaping the future of the AI insurtech market. Insurers are harnessing the power of AI to gain actionable insights from vast amounts of data, improve underwriting processes, and enhance customer engagement through personalized services. As the demand for more efficient, transparent, and customer-centric insurance solutions continues to grow, AI insurtech is expected to play a pivotal role in driving digital transformation across the insurance sector.
In conclusion, the Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market is witnessing rapid growth, driven by the convergence of AI technologies with insurance processes to enhance customer experience, improve operational efficiency, and mitigate risks. The market is characterized by a diverse range of applications, end-users, and market players that are contributing to the innovation and transformation of the insurance industry. As AI continues to reshape the insurance landscape, market players must continue to invest in technology advancements and strategic partnerships to stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of the digital age.The Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market is experiencing a significant transformation driven by the integration of AI technologies into various facets of the insurance sector. One of the key trends shaping the market is the emphasis on enhancing customer experience through innovative solutions such as Chatbots, Customer Behavioral Analytics, and Personalization. Insurance companies are leveraging AI tools to offer tailored services, optimize communication channels, and automate routine tasks, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Moreover, the adoption of AI in Claims Management and Fraud Detection is revolutionizing operational processes within the insurance industry. By automating claims processing and deploying advanced algorithms for fraud detection, insurers can enhance operational efficiency, reduce fraudulent activities, and bolster risk management practices. This focus on operational excellence and risk mitigation is fueling the demand for AI insurtech solutions among insurers, agents, brokers, and other industry stakeholders.
The market landscape is characterized by a diverse ecosystem of players, from established tech giants like IBM, Microsoft, and Google to disruptive insurtech startups such as Lemonade, PolicyBazaar, and Oscar Health. These entities are actively investing in research and development to bolster their AI capabilities and introduce novel solutions that cater to the evolving needs of the insurance landscape. The competitive environment among these players is driving innovation and fostering the creation of cutting-edge AI technologies that are reshaping traditional insurance practices.
Furthermore, the shift towards digitalization and the increasing emphasis on data analytics and predictive modeling are significant drivers influencing the future trajectory of the AI insurtech market. Insurers are leveraging AI to extract actionable insights from vast data sets, enhance underwriting processes, and deliver personalized customer experiences. As the demand for efficient, transparent, and customer-centric insurance solutions grows, AI insurtech is poised to play a critical role in propelling digital transformation across the insurance sector.
In summary, the Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market is witnessing rapid evolution, propelled by the convergence of AI technologies with insurance operations to elevate customer experiences, drive operational efficiencies, and mitigate risks effectively. The market's diverse applications, stakeholders, and innovative approaches are reshaping the insurance industry, necessitating continuous investments in technology advancements and strategic collaborations to stay competitive and meet the evolving demands of the digital era.
Evaluate the company’s influence on the market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-artificial-intelligence-ai-insurtech-market/companies
Forecast, Segmentation & Competitive Analysis Questions for Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market
- How large is the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market currently?
- At what CAGR is the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market projected to grow?
- What key segments are analyzed in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market report?
- Who are the top companies operating in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market?
- What notable products have been introduced recently in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market?
- What geographical data is included in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market analysis?
- Which region is experiencing the quickest growth in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market?
- Which country is forecasted to lead the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market?
- What region currently holds the biggest share of the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Insurtech Market?
- Which country is likely to show the highest growth rate in coming years?
Browse More Reports:
Global OEM Insulation Market
Global Offsite Sterilisation Service Market
Global On Premise Time Tracking Software Market
Global On-Board Charger Market
Global Ophthalmic Packaging Market
Global Organic Asphalt Modifiers Market
Global Organic Food Ingredient Market
Global Ortho-Xylene Market
Global Osteosarcoma Market
Global Over-the-Counter (OTC) Electromagnetic Pulse Therapy Market
Global Package Boilers Market
Global Packaging Tensioner Market
Global Pallet Stretch Wrapping Machine Market
Global Paper Chemicals Market
Global Paper Straw Market
Africa and Saudi Arabia Tools for Road and Bridge Construction Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com
"
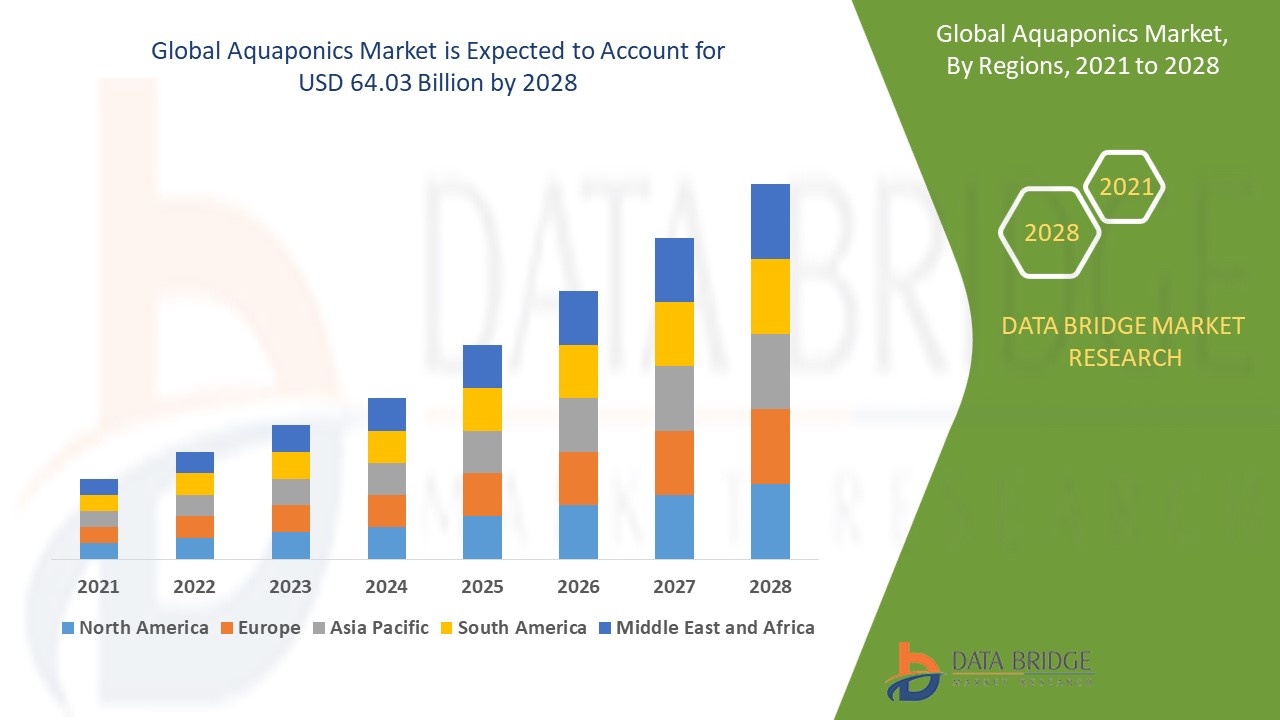 "Key Drivers Impacting Executive Summary Aquaponics Market Size and Share
"Key Drivers Impacting Executive Summary Aquaponics Market Size and Share
Data bridge market research analyses that the aquaponics market will project a compound annual growth rate CAGR of 12.9% during the forecast period of 2021-2028 and account to USD 64.03 billion by 2028.
Accomplishment of maximum return on investment (ROI) is one of the most wannabe goals for any industry which can be achieved with the finest Aquaponics Market research report. Market insights of this report will direct for an actionable ideas, improved decision-making and better business strategies. The main research methodology utilized by DBMR team is data triangulation which entails data mining, analysis of the impact of data variables on the market, and primary validation. The wide ranging report is mainly delivered in the form of PDF and spreadsheets while PPT can also be provided depending upon client’s request. To achieve an inevitable success in the business, Aquaponics Market report plays a significant role.
The large scale Aquaponics Market report helps in determining and optimizing each stage in the lifecycle of industrial process that includes engagement, acquisition, retention, and monetization. This market research report comprises of different industry verticals such as company profile, contact details of manufacturer, product specifications, geographical scope, production value, market structures, recent developments, revenue analysis, market shares and possible sales volume of the company. It helps companies to take decisive actions to deal with threats in the niche market. The dependable Aquaponics Market report presents actionable market insights with which businesses can settle on sustainable and lucrative strategies.
Understand market developments, risks, and growth potential in our Aquaponics Market study. Get the full report:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-aquaponics-market
Aquaponics Industry Trends
**Segments**
- **By Equipment Type**: The aquaponics market can be segmented based on equipment types such as tanks, grow lights, pumps and aeration systems, water heaters, monitoring and control systems, and others. Each of these equipment types plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient functioning of aquaponic systems.
- **By Component**: Components in the aquaponics market include sump, grow bed, fish tank, biofilter, and others. Each component is essential for maintaining a balanced ecosystem within aquaponic setups and facilitating the symbiotic relationship between plants and fish.
- **By Application**: Aquaponics finds applications in commercial, home food production, academic, and research sectors. The versatility of aquaponics allows it to be implemented across various scales, from small-scale setups in homes to large-scale commercial operations.
**Market Players**
- **Nelson and Pade, Inc.**: A prominent player in the aquaponics market, Nelson and Pade, Inc. offers innovative aquaponic systems and solutions for commercial and educational purposes. Their expertise in system design and implementation has positioned them as a key player in the market.
- **The Aquaponic Source**: As a leading supplier of aquaponics equipment and resources, The Aquaponic Source caters to both beginners and experienced aquaponic enthusiasts. Their range of products and educational materials supports the growth of the aquaponics market.
- **ECF Farmsystems**: ECF Farmsystems specializes in sustainable aquaponic farming solutions that focus on reducing environmental impact and maximizing resource efficiency. Their cutting-edge technologies contribute to the advancement of the aquaponics industry.
The global aquaponics market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable agriculture practices and the rising popularity of aquaponic systems among consumers. With key players such as Nelson and Pade, Inc., The Aquaponic Source, and ECF Farmsystems leading the way, the market is witnessing advancements in equipment types and components to enhance system efficiency. The segmentation of the market based on equipment types, components, and applications provides insights into the diverse opportunities present in the aquaponics industry. As technological innovations continue to shape the market landscape, aquaponics is expected to emerge as a key player in the future of agriculture.
Aquaponics is revolutionizing the agriculture industry by offering a sustainable solution that combines aquaculture and hydroponics to create a symbiotic ecosystem. One new insight into the market is the increasing adoption of aquaponics in urban settings. As urban populations grow and land availability for traditional farming diminishes, aquaponic systems present a viable option for cultivating fresh produce locally. This trend is driving innovation in compact and vertical aquaponic setups tailored for urban environments, catering to the demand for fresh, locally sourced food in cities.
Another emerging trend in the aquaponics market is the integration of advanced technologies such as internet of things (IoT) devices and artificial intelligence (AI) for monitoring and control systems. These technologies enable real-time data monitoring, automated adjustments, and predictive analytics, enhancing system efficiency, reducing resource wastage, and optimizing plant growth and fish health. Market players are increasingly investing in research and development to leverage these technologies, leading to the development of smart aquaponic solutions that offer precise control and improved yields.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a growing focus on sustainable practices and environmental stewardship. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the ecological impact of food production, driving the demand for aquaponics as a sustainable farming method. Market players are responding by incorporating eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient components, and recycling systems into their aquaponic setups, aligning with the global shift towards sustainability and reduced carbon footprint in agriculture. This emphasis on sustainability not only appeals to environmentally conscious consumers but also contributes to the overall growth and expansion of the aquaponics market.
Additionally, the integration of aquaponics into educational curriculums and research programs is opening avenues for collaboration and knowledge exchange within the industry. Academic institutions and research organizations are utilizing aquaponic systems as practical teaching tools for students and as platforms for conducting scientific experiments and studies. This educational focus is nurturing a new generation of aquaponics enthusiasts and experts, fostering innovation and driving continuous improvement in system design, operation, and productivity. The collaboration between academia and industry players is fostering a culture of innovation and knowledge sharing that is propelling the aquaponics market forward.
In conclusion, the aquaponics market is experiencing a dynamic shift towards urban farming, technological integration, sustainability initiatives, and educational advancements. These trends are reshaping the industry landscape, expanding market opportunities, and driving innovation in aquaponic systems and practices. As the market continues to evolve and grow, stakeholders should stay attuned to these trends and embrace new developments to capitalize on the vast potential of aquaponics in the future of agriculture.Aquaponics is a rapidly growing sector within the agriculture industry, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable food production methods and the rising popularity of aquaponic systems. One key trend in the market is the shifting focus towards urban farming, where aquaponics is playing a crucial role in enabling local fresh produce cultivation in densely populated areas. The integration of aquaponics in urban settings is fostering innovation in compact and vertical farming setups, catering to the demand for locally sourced food in cities. This trend is not only addressing the challenges of land scarcity but also contributing to food security and promoting a more sustainable food system in urban environments.
Another significant trend in the aquaponics market is the adoption of advanced technologies such as IoT devices and AI for monitoring and control systems. These technologies are revolutionizing aquaponic operations by enabling real-time data monitoring, automated adjustments, and predictive analytics. By enhancing system efficiency, reducing resource wastage, and optimizing plant growth and fish health, these technological integrations are propelling the industry towards heightened productivity and sustainability. Market players are investing in research and development to harness the potential of these smart aquaponic solutions, leading to further advancements in system performance and output.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility within the aquaponics market. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of food production, leading to a surge in demand for sustainable farming practices such as aquaponics. Market players are responding by incorporating eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient components, and recycling systems into their aquaponic setups to align with global sustainability goals. This focus on sustainability not only appeals to environmentally conscious consumers but also positions aquaponics as a key contributor to reducing carbon footprint in agriculture, thus driving market growth and expansion.
Additionally, the integration of aquaponics into educational curriculums and research programs is fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange within the industry. Academic institutions and research organizations are leveraging aquaponic systems as educational tools and scientific platforms, nurturing a new generation of aquaponics enthusiasts and experts. This educational focus is driving innovation, improving system design and operation, and enhancing overall productivity in the aquaponics market. The collaboration between academia and industry players is contributing to a culture of innovation and knowledge-sharing that is propelling the market forward and shaping its future trajectory towards continued growth and development.
Break down the firm’s market footprint
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-aquaponics-market/companies
Aquaponics Market Reporting Toolkit: Custom Question Bunches
- What are the most traded product types?
- How is digitalization reshaping the Aquaponics Market industry?
- How do urban and rural markets differ?
- What export-import trends affect this Aquaponics Market?
- How many patents are filed annually in this space?
- What share of revenue is derived from online channels for Aquaponics Market?
- What CSR initiatives are companies undertaking?
- Which segments show seasonal sales fluctuations?
- How is customer retention being improved?
- What are the recent developments in product packaging?
- How are logistics challenges being addressed?
- What is the ROI for major players for Aquaponics Market?
- What are the top-performing sales channels for Aquaponics Market?
- How has the pandemic affected supply and demand for Aquaponics Market?
Browse More Reports:
Global Muckle Wells Syndrome Market
Global Mussel Oil Market
Global N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine Market
Global Nanoencapsulation Market
Global Nasal Spray Packaging Component Market
Global Neglected Tropical Diseases Treatment Market
Global Network Attached AI Storage System Market
Global Neurodiagnostics Market
Global Neurotrophic Keratitis Treatment Market
Global Next Generation Matting Agents Market
Global Non-destructive Testing Services and Equipment Market
Global Non-volatile Memory Express Market
Global Nucleotides Supplements Market
Global Nuts Trail Mixes Market
Global Obesity Treatment Market
Middle East and Africa Lymphedema Treatment Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com
"
Air Filters Market Competitive Landscape – Key Players & Strategic Developments
By dannykinggt, 2025-08-18
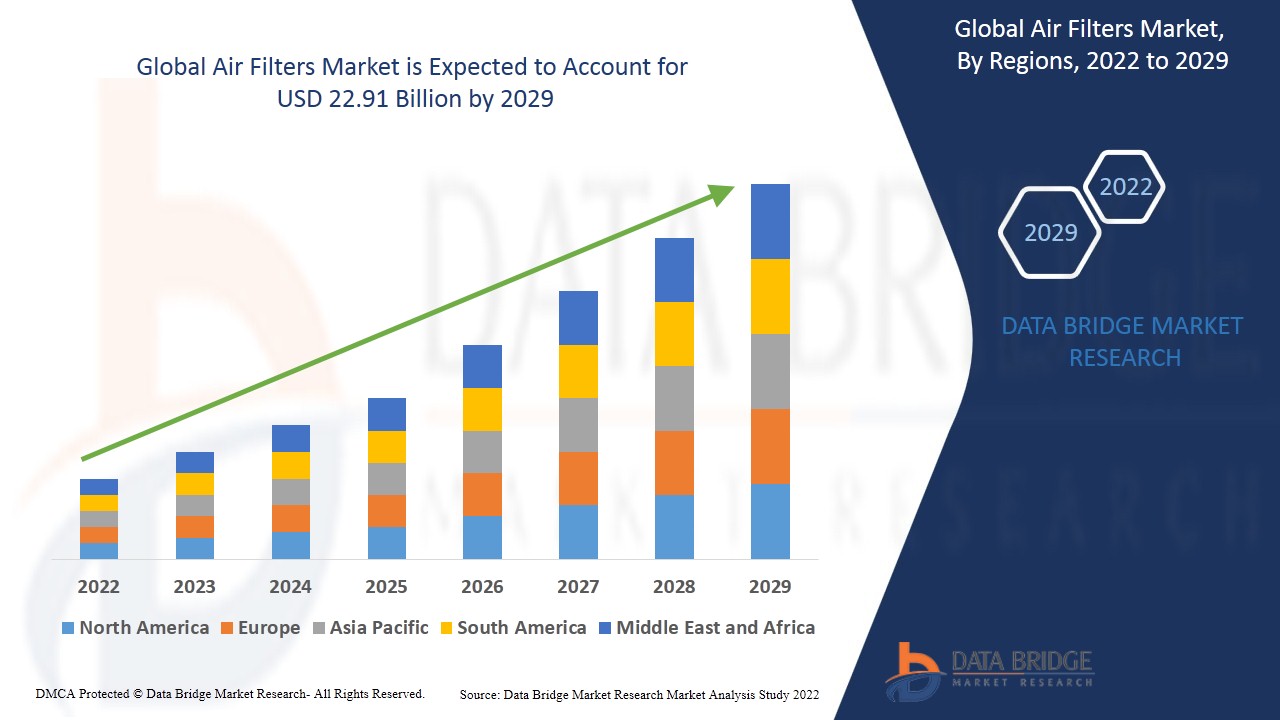 "Executive Summary Air Filters Market Research: Share and Size Intelligence
"Executive Summary Air Filters Market Research: Share and Size Intelligence
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the air filters market would exhibit a CAGR of 5.30% for the forecast period of 2022-2029.
Best-practice models and research methodologies have been employed in the reliable Air Filters Market report for a complete market analysis. It is a completely informative and proficient report that highlights primary and secondary market drivers, market share, leading segments and geographical analysis. With this business report, it has been assured that an absolute knowledge and insights about the new regulatory environment which are most suitable for their organization are provided. Utilization of integrated approaches combined with most up-to-date technology for building this world class marketing report makes it unrivalled. The trends in consumer and supply chain dynamics are acknowledged in Air Filters Market report to accordingly interpret the strategies about marketing, promotion and sales.
With the market info provided in the global Air Filters Market report, it has become easy to gain global perspective for the international business. Focus groups and in-depth interviews are included for qualitative analysis whereas customer survey and analysis of secondary data has been carried out under quantitative analysis. This market research report acts as a very significant constituent of business strategy. This market report is a definite study of the Air Filters Market industry which explains what the market definition, classifications, applications, engagements, and global industry trends are. Air Filters Market report proves to be a sure aspect to help grow the business.
Find out what’s next for the Air Filters Market with exclusive insights and opportunities. Download full report:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-air-filters-market
Air Filters Market Dynamics
**Segments**
- By Type: HEPA Filters, Activated Carbon Filters, Pre Filters, Electrostatic Filters, UV Filters, Ionic Filters, Others
- By End-User: Residential, Commercial, Industrial
- By Application: HVAC Systems, Industrial Filtration, Residential, Others
The global air filters market is segmented based on type, end-user, and application. In terms of type, the market is categorized into HEPA filters, activated carbon filters, pre filters, electrostatic filters, UV filters, ionic filters, and others. HEPA filters are known for their high efficiency in removing airborne particles, making them suitable for applications where air quality is crucial. Activated carbon filters are effective in removing odors and harmful gases. Pre filters are used as the first line of defense in capturing large particles. Electrostatic filters use static electricity to trap particles. UV filters are known for their ability to kill bacteria and viruses, while ionic filters work by ionizing particles to attract them. The market segments based on end-user include residential, commercial, and industrial. The residential sector includes households and small offices, while the commercial sector comprises hospitals, schools, malls, and other public places. The industrial sector covers various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. When it comes to applications, the market is segmented into HVAC systems, industrial filtration, residential use, and others.
**Market Players**
- Camfil
- Parker Hannifin Corp
- Mann+Hummel
- Donaldson Company, Inc.
- Clarcor Inc.
- Daikin Industries, Ltd.
- 3M
- Ahlstrom-Munksjö
- Freudenberg Filtration Technologies
- Dafco Filtration Group
- Filtration Group Corporation
- Cummins, Inc.
- Lennox International, Inc.
The global air filters market consists of several key players who are actively involved in product development, innovation, and strategic partnerships. Some of the prominent market players in the industry are Camfil, Parker Hannifin Corp, Mann+Hummel, Donaldson Company, Inc., Clarcor Inc., Daikin Industries, Ltd., 3M, Ahlstrom-Munksjö, Freudenberg Filtration Technologies, Dafco Filtration Group, Filtration Group Corporation, Cummins, Inc., and Lennox International, Inc. These companies are focusing on expanding their product portfolios, enhancing their distribution networks, and investing in research and development to introduce advanced filtration technologies. By leveraging strategic collaborations and mergers, these market players are aiming to strengthen their market presence and cater to the growing demand for air filters across various industries.
The global air filters market is witnessing significant growth driven by various factors such as increasing awareness about indoor air quality, stringent government regulations regarding air pollution, and rising concerns about health issues related to poor air quality. The demand for air filters is on the rise across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors as consumers prioritize cleaner and healthier air environments. With the emergence of advanced filtration technologies and the need to combat pollutants, the market is experiencing a shift towards more efficient and specialized air filters. HEPA filters remain a popular choice due to their high efficiency in capturing particles, especially in environments where air purity is crucial, such as hospitals and clean rooms. Activated carbon filters are favored for their ability to eliminate odors and harmful gases, making them suitable for commercial spaces like restaurants and office buildings. Electrostatic filters and UV filters are gaining traction for their unique mechanisms in trapping particles and sterilizing air, respectively.
In terms of end-users, the residential sector is a significant contributor to the air filters market as homeowners seek to improve the air quality in their living spaces. The commercial sector, encompassing a wide range of establishments from schools to shopping malls, is also a key consumer of air filters to maintain a clean and safe environment for occupants. The industrial segment plays a crucial role in driving market growth, with industries such as manufacturing and automotive requiring efficient filtration solutions to meet regulatory standards and ensure worker safety. HVAC systems are a primary application area for air filters, as they are integral to maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and air quality in buildings. Industrial filtration applications involve filtering out contaminants in manufacturing processes, while residential users rely on air filters for cleaner air at home.
Key market players like Camfil, Parker Hannifin Corp, and Mann+Hummel are continuously investing in research and development to introduce advanced filtration technologies that address evolving consumer needs and regulatory requirements. These companies are also focusing on expanding their global footprint through strategic partnerships and acquisitions to gain a competitive edge in the market. With the increasing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, the air filters market is expected to witness further innovation in eco-friendly filter solutions and smart technologies that enhance air quality monitoring and control. The global air filters market is poised for continued growth as the importance of clean air becomes a top priority for individuals and industries worldwide.The global air filters market is highly competitive, with key players such as Camfil, Parker Hannifin Corp, and Mann+Hummel leading the industry through innovation and strategic partnerships. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to introduce advanced filtration technologies that cater to the evolving needs of consumers and regulatory requirements. By expanding their product portfolios, enhancing distribution networks, and focusing on sustainability and energy efficiency, these market players are positioning themselves as industry leaders in the air filters market. Additionally, strategic collaborations and mergers play a crucial role in strengthening market presence and meeting the growing demand for air filters across various end-user segments and applications.
One of the key drivers of market growth is the increasing awareness about indoor air quality and the health implications of poor air. As consumers become more conscious of the importance of clean and healthy air environments, the demand for air filters is rising across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. The stringent government regulations concerning air pollution further contribute to the market expansion, as companies and industries are required to adhere to quality standards and ensure the well-being of occupants. Advanced filtration technologies such as HEPA filters, activated carbon filters, electrostatic filters, and UV filters are witnessing increased adoption due to their efficiency in capturing particles and improving air quality in various settings.
In terms of end-users, residential households are a significant contributor to the air filters market as homeowners prioritize creating a safe and clean living environment for their families. The commercial sector, including hospitals, schools, malls, and offices, also plays a vital role in driving market growth by investing in air filtration solutions to maintain a healthy indoor atmosphere for employees and customers. Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace utilize air filters to meet regulatory standards, ensure worker safety, and enhance the quality of production processes. HVAC systems and industrial filtration applications are primary areas where air filters are essential for maintaining optimal air quality and operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, the global air filters market is poised for continued growth as the emphasis on clean air and environmental sustainability intensifies worldwide. Market players will continue to focus on research and development, strategic partnerships, and technological advancements to address the increasing demand for advanced filtration solutions. With a shift towards eco-friendly filter solutions and smart technologies that enhance air quality monitoring and control, the market is expected to witness further innovation and adoption of specialized air filters across diverse industries and applications. As clean air becomes a top priority for individuals and businesses, the air filters market is projected to experience sustained growth and evolution in the coming years.
Track the company’s evolving market share
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-air-filters-market/companies
Master List of Market Research Questions – Air Filters Market Focus
- How large is the addressable market in terms of volume?
- What is the average revenue per user (ARPU)?
- How many startups are entering the Air Filters Market yearly?
- What are the growth drivers in developing economies?
- What is the impact of e-commerce on this Air Filters Market?
- What consumer preferences are influencing product design?
- Which demographic segments are being targeted?
- How are supply chains evolving in this Air Filters Market?
- Which regions are witnessing price wars?
- What is the typical lifecycle of a product in this Air Filters Market?
- How sustainable is the production process in this Air Filters Market industry?
- Which companies have increased R&D spending?
- What impact does inflation have on demand?
- How do marketing strategies vary globally Air Filters Market?
Browse More Reports:
Global Medical Vacuum System Market
Global Membrane Chromatography Market
Global Menkes Syndrome Market
Global Metal Carboxylate Market
Global Metallic Microspheres Market
Global Methylxanthines Market
Global Microcontroller for Parking Assist System Market
Global Micro-Perforated Food Packaging Market
Global Middle Ear Implants Market
Global Minimally Invasive Medical Robotics, Imaging and Visualization Systems and Surgical Instruments Market
Global Mining Waste Management Market
Global Miticides for Fruits and Vegetables Market
Global Model-based Enterprise Market
Global Moles Treatment Market
Global Mortuary Equipment Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- corporatesales@databridgemarketresearch.com
"