Report Overview:
The global
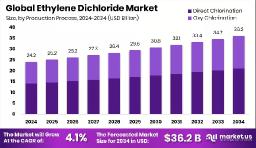
Ethylene Dichloride Market is projected to reach approximately
USD 36.2 billion by 2034, rising from an estimated
USD 24.2 billion in 2024. This growth reflects a compound annual growth rate
(CAGR) of 4.1% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
North America continues to hold a dominant position in the market, accounting for
39.10% of the global EDC demand, supported by its well-established industrial infrastructure.
The global ethylene dichloride (EDC) market is experiencing steady growth, driven primarily by its crucial role in the production of vinyl chloride monomer (VCM), a key precursor to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). With increasing demand from the construction, automotive, and packaging sectors, EDC consumption continues to rise. The market is further supported by industrial expansion in developing economies and advancements in chlorination technologies. North America and Asia-Pacific remain dominant regions, benefiting from strong manufacturing infrastructures and rising end-use demand. However, environmental regulations and health concerns present ongoing challenges, pushing the industry toward cleaner, more sustainable production methods.
Key Takeaways:
- Global Ethylene Dichloride Market is expected to be worth around USD 36.2 billion by 2034, up from USD 24.2 billion in 2024, and grow at a CAGR of 4.1% from 2025 to 2034.
- The Ethylene Dichloride market is largely driven by direct chlorination, accounting for 58.3% share.
- Vinyl chloride monomer production remains the leading application in the Ethylene Dichloride market at 82.4%.
- Construction leads as the largest end-use sector in the Ethylene Dichloride market, holding 45.9% share.
- Ethylene Dichloride market in North America reached a value of USD 9.4 billion.
 https://market.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Ethylene-Dichloride-Market-Size.jpg" alt="Ethylene Dichloride Market Size" width="1216" height="706">
https://market.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Ethylene-Dichloride-Market-Size.jpg" alt="Ethylene Dichloride Market Size" width="1216" height="706">
Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/global-ethylene-dichloride-market/free-sample/
Key Market Segments:
By Production Process
- Direct Chlorination
- Oxy Chlorination
By Application
- Vinyl Chloride Monomer
- Ethylene Amines
- Others
By End-Use
- Construction
- Automotive
- Packaging
- Furniture
- Medical
- Others
Drivers
The ethylene dichloride (EDC) market is primarily driven by its critical role in the production of vinyl chloride monomer (VCM), which is a precursor to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC’s wide-ranging use across the construction, automotive, packaging, and electrical industries is the core force behind consistent EDC demand. In particular, the construction sector remains the largest consumer of PVC due to its application in pipes, fittings, window frames, and flooring. As new construction projects and infrastructure upgrades continue across both developed and emerging markets, the downstream demand for PVC and therefore EDC is expected to rise steadily.
Another key driver is industrial expansion in high-growth regions, especially in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. These regions are investing heavily in manufacturing facilities, smart cities, and transportation infrastructure, all of which require large volumes of durable plastic materials. EDC, as an upstream raw material, benefits directly from this industrial momentum. Additionally, increased adoption of lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials in automotive production has expanded the use of PVC in vehicle interiors, wire harnesses, and under-the-hood applications, indirectly supporting EDC consumption.
The rising adoption of chlorinated solvents and intermediates in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors also contributes to EDC demand. While VCM production dominates, EDC’s versatility as a solvent in closed systems and as a chemical intermediate gives it relevance in specialty applications.
Restraining Factors
Despite its widespread industrial applications, the ethylene dichloride (EDC) market faces several restraining factors that could limit its long-term growth potential. One of the most significant challenges is the tightening of environmental and health regulations. EDC is classified as a hazardous chemical due to its toxic, flammable, and carcinogenic nature. This has led to stricter handling, storage, and transportation guidelines, particularly in regions like North America and Europe, where environmental standards are becoming more stringent.
Governments and regulatory agencies are increasingly emphasizing emission control and waste management across chemical manufacturing sectors. Producers of EDC are under pressure to comply with guidelines related to air pollutants, wastewater discharge, and occupational safety. These compliance requirements often involve high capital investment in cleaner technologies, emissions monitoring systems, and closed-loop processing, thereby raising production costs and potentially deterring new entrants. In addition, volatile raw material prices especially for feedstocks like ethylene and chlorine can significantly impact production margins.
EDC is typically produced through chlorination processes, and any fluctuations in raw material supply chains or energy costs can create pricing instability, affecting profitability and market consistency. Public health concerns also play a growing role. With rising awareness of chemical exposure risks, local communities and environmental groups are placing pressure on industries to phase out or substitute potentially harmful substances. While EDC remains essential for PVC production, this social and political push for safer alternatives could lead to a gradual shift toward bio-based or less toxic materials in the long run.
Opportunities
One of the most promising growth opportunities in the global ethylene dichloride (EDC) market stems from the rapid pace of urbanization and infrastructure expansion. EDC is a key raw material in the production of vinyl chloride monomer (VCM), which is then polymerized into polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Given PVC’s widespread use in construction applications such as piping, window frames, roofing membranes, and insulation the ongoing boom in infrastructure projects is directly boosting demand for EDC.
According to the United Nations, approximately 57% of the world’s population lives in urban areas as of 2024, and this figure is expected to rise to 68% by 2050. This urban shift is especially significant in developing regions like Asia, Africa, and Latin America, where rapid industrialization and population growth are placing immense pressure on housing and public infrastructure. As a result, governments are heavily investing in long-term infrastructure programs. For example, India’s Smart Cities Mission and China’s Belt and Road Initiative are channeling billions of dollars into urban development, water management, and housing all sectors reliant on PVC components.
PVC is known for its low cost, long life span, and ease of installation, making it a preferred material in both residential and industrial projects. In turn, this drives up the need for VCM and consequently EDC. It is estimated that over 95% of global EDC production is used for VCM, showcasing the direct correlation between urban development and EDC demand. As infrastructure becomes a top priority globally whether for housing, transport, or utilities the need for cost-effective materials like PVC ensures a stable and growing market for EDC. This trend is expected to remain strong throughout the next decade, offering consistent opportunity for producers and investors alike.
Trends
Shaping the ethylene dichloride (EDC) market is the growing emphasis on cleaner, more energy-efficient production processes. With EDC production heavily reliant on chlorination methods primarily direct chlorination and oxychlorination manufacturers are increasingly optimizing technologies to reduce emissions, minimize energy use, and limit chlorinated byproduct generation. As of 2024, direct chlorination accounts for nearly 58.3% of global EDC production, according to Market.us.
This method remains popular due to its higher yield and cost-efficiency when paired with integrated ethylene and chlorine feedstocks. However, the oxychlorination process which combines hydrogen chloride and oxygen with ethylene is gaining attention for its environmental advantages. It helps recycle hydrogen chloride, a byproduct of vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) production, thus reducing waste and improving sustainability across the value chain.
Several chemical manufacturers are investing in advanced reactor designs and catalytic systems that lower operating temperatures and reduce energy consumption. This aligns with increasing regulatory pressure in regions like Europe and North America, where emissions from chlorinated hydrocarbon production are tightly monitored. In parallel, EDC is finding niche applications beyond its dominant role in VCM production.
Although more than 82% of EDC is consumed for VCM, its use as a solvent in closed-loop systems, intermediate for organic synthesis, and extraction agent in pharmaceuticals and adhesives is slowly expanding. These niche applications are particularly relevant in sectors like agrochemicals, resins, and specialty coatings.
Market Key Players:
- Axiall Corporation
- Formosa Plastics Corporation
- Horizon Chemical Industry Co. Ltd
- INEOS Group Holdings S.A.
- LyondellBasell Industries N.V.
- Occidental Petroleum Corporation
- Olin Corporation
- PPG Industries
- PT Asahimas Chemical
- Punjab Chemicals & Crop Protection Limited
- Saudi Basic Industries Corporation
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Westlake Chemical Corporation
Conclusion
The ethylene dichloride (EDC) market is positioned for sustained growth, largely due to its indispensable role in producing vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) and, ultimately, polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The growing demand for durable, low-cost construction materials particularly in rapidly urbanizing regions continues to drive consumption. Infrastructure projects, housing development, and industrial expansion across Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa are key contributors to market momentum. At the same time, developed regions such as North America remain significant due to established chemical manufacturing capabilities. However, challenges such as regulatory pressures, environmental concerns, and the hazardous nature of EDC cannot be overlooked.
These factors are prompting shifts toward cleaner technologies and more sustainable operational practices. Looking ahead, the market will likely evolve alongside advances in production efficiency, circular economy practices, and emerging applications outside of VCM. With the right investments and innovations, the EDC market can balance both growth potential and environmental responsibility.

https://market.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Ethylene-Dichloride-Market-Size.jpg" alt="Ethylene Dichloride Market Size" width="1216" height="706">