Report Overview:
The
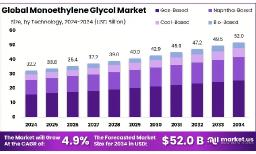
Global Monoethylene Glycol Market is projected to reach approximately
USD 52.0 billion by 2034, up from
USD 32.2 billion in 2024, registering a compound annual growth rate
(CAGR) of 4.9% between 2025 and 2034.
Monoethylene glycol (MEG) is a vital intermediate in the petrochemical industry, primarily used in the production of polyester fibers and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resins. It is produced through the hydration of ethylene oxide, which is derived from ethylene. Conventional production methods typically achieve around 90% MEG purity, with the remainder consisting of byproducts like diethylene glycol and triethylene glycol. However, newer technologies, such as the Shell OMEGA process licensed from Mitsubishi, have improved selectivity to over 99%. These advanced processes reduce unwanted byproducts and lower energy consumption, enhancing overall efficiency and environmental performance in MEG production.
Key Takeaways:
- Monoethylene Glycol Market size is expected to be worth around USD 52.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 32.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.9%.
- Gas-Based technology held a dominant market position in the global monoethylene glycol (MEG) market, capturing more than a 49.3% share.
- Polyester Fibers held a dominant market position in the global monoethylene glycol (MEG) market, capturing more than a 59.1% share.
- Textile held a dominant market position in the global monoethylene glycol (MEG) market, capturing more than a 56.8% share.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region stands as the dominant force in the global Monoethylene Glycol (MEG) market, commanding a substantial share of 42.9%, equating to approximately USD 13.8 billion.

https://market.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Monoethylene-Glycol-Market.jpg" alt="Monoethylene Glycol Market" width="1216" height="736">
Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/global-monoethylene-glycol-market/free-sample/
Key Market Segments:
By Technology
- Gas-Based
- Naphtha-Based
- Coal-Based
- Bio-Based
By Application
- PET
- Polyester Fibers
- Antifreeze
- Others
By End-use
- Textile
- Packaging
- Automotive
- Plastics
- Other
Drivers
The global monoethylene glycol (MEG) market is experiencing significant momentum, largely propelled by rising demand from the polyester and packaging industries. One of the primary growth drivers is the expanding use of polyester fibers, which account for a major portion of MEG consumption worldwide. As global textile production increases particularly in fast-growing economies like China, India, Vietnam, and Bangladesh the demand for MEG as a key raw material in polyester manufacturing continues to surge.
Polyester fibers are used not only in clothing but also in home furnishings, industrial textiles, and non-woven fabrics, all of which are seeing steady demand growth. Additionally, the widespread use of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resins in food and beverage packaging especially bottles and containers is further fueling MEG consumption. With global plastic bottle usage estimated to exceed 500 billion units per year, and increasing pressure on lightweight, recyclable packaging, MEG remains an essential feedstock for PET production.
The rising popularity of bottled water, carbonated drinks, and ready-to-drink beverages continues to add pressure on PET production, directly influencing MEG demand. Government initiatives supporting domestic manufacturing and sustainability are also playing a pivotal role. Countries like China have implemented policies favoring local PET production and the use of cleaner energy sources for chemical manufacturing. Similarly, in regions like North America and Europe, R&D funding and tax incentives are encouraging the development of more energy-efficient MEG production technologies, including gas-based and bio-based routes.
Restraining Factors
While the MEG market is projected to grow steadily, several restraining factors could limit its pace of expansion. One of the most significant constraints is the volatility in raw material prices, especially ethylene and natural gas. These feedstocks are derived from crude oil and natural gas, both of which are highly sensitive to global geopolitical tensions, trade policies, and supply chain disruptions. For instance, during periods of oil price spikes, MEG producers face rising input costs that directly impact their profit margins.
Another challenge stems from the environmental impact of traditional MEG production. Conventional manufacturing methods generate significant carbon emissions and chemical byproducts like diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG), which require additional processing or disposal. As global environmental regulations tighten particularly in Europe and North America compliance costs for MEG producers are increasing. Regulatory bodies are also introducing stricter limits on emissions, water usage, and waste disposal, making it more difficult for legacy facilities to operate profitably.
Additionally, the rise of recycled PET (rPET) and the circular economy movement is slowly impacting virgin MEG demand. Many packaging and textile companies are shifting toward using recycled materials, which reduces the need for fresh MEG in PET production. As sustainability becomes central to product development and brand strategy, the demand for virgin MEG could face longer-term structural challenges. Finally, overcapacity in certain regions, particularly in Asia-Pacific, has led to downward pressure on MEG prices. Several large-scale projects have come online in recent years, increasing global supply faster than demand growth. This imbalance may result in reduced profitability for manufacturers and limit future investment.
Opportunities
The global monoethylene glycol (MEG) market is entering a new phase of growth, driven by the emergence of bio-based and waste-derived production methods. These alternative routes offer promising opportunities to reduce dependency on fossil fuels, improve cost-efficiency, and meet growing environmental regulations. With global pressure mounting for sustainable chemical processes, the shift toward green MEG is becoming a viable and attractive option for both producers and investors. Bio-based MEG, derived from renewable feedstocks like sugarcane, corn, and agricultural residues, has gained attention due to its lower carbon footprint.
Companies across the U.S., Brazil, and parts of Europe are exploring commercial-scale production of bio-MEG, which can seamlessly replace traditional MEG in polyester and PET applications. According to industry estimates, using bio-MEG can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 60% compared to conventional methods. This aligns well with sustainability targets set by major packaging and textile brands, many of whom aim for 100% recyclable or bio-based packaging by 2030.
Another promising opportunity lies in waste-to-chemical technologies. Pilot projects are now exploring the conversion of plastic waste or municipal solid waste (MSW) into syngas, which can then be used to produce MEG. Such methods not only offer a second life to plastic waste but also reduce landfill pressure and emissions. Moreover, integrated production units where ethylene oxidation and hydration processes are combined in a single setup are being tested to improve energy efficiency and streamline operations.
These systems have the potential to reduce operational costs by 15-20% and minimize byproducts like diethylene glycol (DEG). With growing regulatory and consumer pressure for low-carbon alternatives, producers that invest early in bio-based or waste-derived MEG technologies could gain a strategic edge. These innovations are expected to unlock new revenue streams while supporting the global transition toward circular and sustainable chemical production.
Trends
The MEG industry is currently undergoing a transformative shift, driven by sustainability, technological innovation, and evolving end-use demand. One of the most prominent trends is the rising adoption of bio‑based MEG. Industries such as textiles, packaging, and automotive are increasing their reliance on this eco‑friendly alternative, drawn by its lower lifecycle emissions and alignment with regulatory standards.
Bio‑MEG now offers up to 60-70% lower CO₂ intensity than conventional petrochemical MEG, making it essential for Scope 3 emission reporting frameworks like CSRD and ISSB. In parallel, production technology is evolving rapidly. Advances in catalytic and separation processes like Shell’s OMEGA process enable higher yield, reduced energy use, and minimal waste.
These improvements help cut costs and meet growing demand efficiently, enhancing both performance and sustainability. Geographical trends are significantly influencing the global MEG market. The Asia-Pacific region, with China and India at the forefront, leads global MEG consumption. This dominance is attributed to the presence of large-scale textile and packaging industries, as well as expanding automotive manufacturing hubs. In 2022, Asia-Pacific accounted for nearly 60% of the global market share, largely due to increased polyester fiber production and infrastructural development across emerging economies.
Market Key Players:
- Acuro Organics Ltd.
- Arham Petrochem Pvt. Ltd.
- BASF SE
- Dow
- Euro Industrial Chemicals
- India Glycols Limited
- Indian Oil Corporation Ltd.
- Ishtar Company, LLC
- Kimia Pars Co.
- LyondellBasell N.V.
- MEGlobal
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Nan Ya Plastics Corporation
- Nouryon
- Pon Pure Chemicals Group
Conclusion
The monoethylene glycol (MEG) market faces several operational and regulatory challenges. Price volatility in key raw materials such as natural gas and ethylene continues to impact production margins. These feedstocks, being directly linked to global oil and gas trends, are subject to supply disruptions and geopolitical factors. Additionally, stricter environmental regulations in regions like Europe and North America are increasing compliance requirements for MEG producers, particularly concerning emissions and waste management.
The growing use of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (RPET) is also influencing MEG demand. As industries adopt more circular practices, the reliance on virgin MEG for PET resin production may decline. This shift could affect future consumption patterns and pricing structures across key sectors. Despite these pressures, producers are gradually transitioning toward integrated and bio-based production methods. Investment in research and development is ongoing, focused on improving process efficiency and reducing environmental impact while ensuring stable supply to downstream industries.