Report Overview:
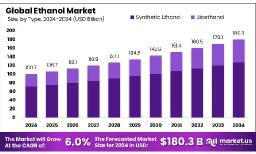
The Global Ethanol Market is projected to reach approximately USD 180.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 100.7 billion in 2024, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The global ethanol market is steadily growing, fueled by increasing demand for renewable energy and environmentally friendly industrial solutions. Ethanol, a plant-derived alcohol typically made from corn, sugarcane, and other biomass, is widely used as a fuel additive, solvent, and ingredient in sectors like pharmaceuticals, personal care, and beverages. Its ability to lower greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to energy independence has made it an essential component in many countries’ sustainability efforts. With government support, advances in biofuel production, and expanding use across both energy and non-energy industries, the ethanol market is poised for continued growth in the years ahead.
Key Takeaways:
- The Global Ethanol Market is projected to grow from USD 100.7 billion in 2024 to USD 180.3 billion by 2034, at a 6.0% CAGR.
- Synthetic ethanol dominates the market by type, holding over 71.2% share due to cost-effective production and industrial use.
- Denatured ethanol leads in purity, capturing 59.2% share, driven by its use in industrial and fuel applications.
- Corn is the top source for ethanol, holding a 48.2% share, supported by strong biofuel demand and agricultural infrastructure.
- Fuel is the largest application segment, with a 41.1% share, as ethanol is widely used as a renewable fuel additive.
- North America leads the ethanol market with a 48.2% share, generating USD 48.5 billion, driven by the U.S. as the top producer and consumer.
https://market.us/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Ethanol-Market-1.jpg" alt="Ethanol Market" width="1216" height="734">Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/ethanol-market/free-sample/
Key Market Segments:
By Type
- Synthetic Ethanol
- Bioethanol
By Purity
- Denatured
- Undenatured
By Source
- Corn
- Sugarcane
- Wheat
- Cellulose
- Petrochemical
- Others
By Application
- Pharmaceuticals
- API
- Disinfectants
- Herbal Medicinal Products
- Syrups
- Others
- Fuel
- E5
- E10
- E15 to E70
- E75 and E85
- Others
- Personal Care and Cosmetics
- Perfumes and Fragrances
- Hair Care
- Hygiene Products
- Skin Care
- Others
- Beverages
- Chemicals
- Others
Drivers
The ethanol market is gaining momentum globally, largely due to the rising demand for cleaner, renewable alternatives to fossil fuels. A key growth driver is the increasing adoption of ethanol-blended fuels in the transportation industry. Many governments are implementing policies that mandate blending ethanol with gasoline like E10, E15, or E20 to reduce harmful emissions and lower oil dependency. This is particularly prevalent in regions with strong agricultural sectors and ambitious sustainability goals.
The widespread availability of agricultural feedstocks such as sugarcane, corn, and wheat also supports ethanol production, making use of surplus crops that might otherwise go to waste. This aligns with circular economy initiatives and enhances the overall value chain.
Beyond fuel, ethanol is seeing greater demand in industrial applications. Its use in pharmaceuticals, personal care, and chemical industries continues to grow, thanks to its low toxicity, biodegradability, and effectiveness as a solvent. The COVID-19 pandemic also gave ethanol an additional boost as a primary ingredient in sanitizers and disinfectants, opening new doors in health and hygiene-related markets.
Restraining Factors
Despite its growth, the ethanol market faces several barriers. One of the main challenges is the volatility in feedstock prices. Since ethanol production relies heavily on crops like corn and sugarcane, fluctuations in agricultural yields due to weather events or geopolitical disruptions can lead to unstable production costs and pricing.
Another key concern is the ongoing debate over the use of food crops for fuel. In regions dealing with food insecurity, prioritizing crops for ethanol instead of human consumption raises both ethical and economic questions. This “food versus fuel” dilemma could lead to policy shifts and reduced government support.
Infrastructure also poses a challenge. Many countries lack the necessary facilities like blending stations and distribution networks for large-scale ethanol use. Modifying existing infrastructure or upgrading vehicles to accommodate higher ethanol blends requires significant investment, which not all regions are ready to make.
Moreover, ethanol has a lower energy density than gasoline. This means that vehicles travel shorter distances per liter, making it less attractive when oil prices are low and consumers focus on cost-efficiency over environmental benefits.
Opportunities
There are promising growth avenues for ethanol, especially with the rise of low-carbon initiatives. One key opportunity lies in second-generation (2G) ethanol, which is made from non-food biomass such as crop residues, forestry waste, and organic municipal waste. This approach avoids the food-versus-fuel conflict and supports sustainable waste management.
Another growing opportunity is the use of ethanol in green chemistry. It’s increasingly being used as a building block for producing bio-based chemicals like ethyl acetate and acetic acid critical in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial formulations. Ethanol’s eco-friendly nature gives it an edge as a replacement for petroleum-derived inputs.
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia, Latin America, and Africa, are launching or expanding ethanol blending programs to reduce reliance on imported oil. These regions offer untapped potential for both local production and international ethanol trade.
Ethanol also has potential in aviation. Efforts are underway to convert ethanol into sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), offering a new path for decarbonizing air travel. With global aviation sectors targeting net-zero emissions, ethanol’s role in SAF could expand dramatically in the coming years.
Trends
One of the most significant trends in the ethanol market is the shift toward second-generation ethanol made from agricultural and forestry residues. This type of ethanol is more sustainable and cost-effective. In regions like North America, more than half of cellulosic ethanol now comes from crop waste like corn stover. Asia-Pacific is also accelerating production, driven by growing environmental awareness and policy support.
Blending mandates are also evolving. For example, Brazil recently increased its ethanol blend rate in gasoline from 27% to 30%, leading to a spike in corn-based ethanol output. In India, the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program reached 16.2% in 2024, supported by the development of thousands of new E20 fuel stations.
Another emerging trend is ethanol's entry into the sustainable aviation fuel space. Projects like a U.S.-based facility expected to produce 250 million gallons annually highlight ethanol's growing importance in reducing airline emissions.
The market is also seeing diversification. Ethanol use in industrial applications including disinfectants, cleaners, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals grew significantly in 2024, accounting for over 7 billion liters globally. This trend shows that ethanol is expanding well beyond fuel, finding roles in a wide range of sustainable, high-demand industries.
Market Key Players:
- The Archer Daniels Midland Company
- POET, LLC
- Valero Energy Corporation
- Green Plains
- Advanced BioEnergy LLC
- Cargill, Incorporated
- INEOS
- HBL
- LyondellBasell Industries
- Sasol
- Marquis Energy LLC
- Pannonia Bio
- BIOAGRA SA
- Balrampur Chini Mills Ltd
- Shree Renuka Sugars Ltd
- The Andersons Inc.
- Bajaj Hindusthan Limited
- Triveni Group
- Raízen
Conclusion
The global ethanol market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for cleaner fuels and sustainable, bio-based solutions. As nations aim to lower carbon emissions and adopt greener energy strategies, ethanol has emerged as a key component both as a renewable fuel additive and as an eco-friendly solvent. Its broad range of applications across industries like transportation, pharmaceuticals, personal care, and food processing adds to its growing importance.
Moreover, advancements in production technologies, especially the development of second-generation ethanol using agricultural waste, are enhancing efficiency and reducing reliance on traditional feedstocks. These innovations support circular economy goals and help build a more resilient supply chain. Ongoing regulatory support and increased consumer focus on environmental sustainability continue to drive global ethanol demand forward.